Performance Evaluation of Developed Bangasure™ Multiplex rRT-PCR Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Bangladesh: A Blinded Observational Study at Two Different Sites
- PMID: 36359461
- PMCID: PMC9689614
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12112617
Performance Evaluation of Developed Bangasure™ Multiplex rRT-PCR Assay for SARS-CoV-2 Detection in Bangladesh: A Blinded Observational Study at Two Different Sites
Abstract
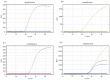
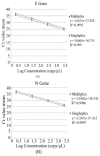
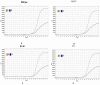
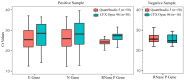
In this study, we evaluated the performance of the in-house developed rRT-PCR assay for SARS-CoV-2 RNA targeting the envelope (E) and nucleocapsid (N) genes with internal control as human RNase P. A total of 50 positive samples and 50 negative samples of SARS-CoV-2 were tested by a reference kit at site 1 and a subset (30 positives and 16 negatives) of these samples are tested blindly at site 2. The limit of detection (LoD) was calculated by using a replication-deficient complete SARS-CoV-2 genome and known copy numbers, where Pseudo-virus samples were used to evaluate accuracy. On site 1, among the 50 SARS-CoV-2 positive samples 24, 18, and eight samples showed high (Ct < 26), moderate (26 < Ct ≤ 32), and low (32 < Ct ≤ 38) viral load, respectively, whereas in site 2, out of 30 SARS-CoV-2 positive samples, high, moderate, and low viral loads were found in each of the 10 samples. However, SARS-CoV-2 was not detected in the negative sample. So, in-house assays at both sites showed 100% sensitivity and specificity with no difference observed between RT PCR machines. The Ct values of the in-house kit had a very good correlation with the reference kits. LoD was determined as 100 copies/mL. It also displayed 100% accuracy in mutant and wild-type SARS-CoV-2 virus. This Bangasure™ RT-PCR kit shows excellent performance in detecting SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA compared to commercially imported CE-IVD marked FDA authorized kits.
Keywords: Bangasure™; LoD; Nucleocapsid; SARS-CoV-2; rRT-PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that RT-PCR kit production and distribution would be done by BRiCM, a statutory body under the Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh at production cost. Hence all the authors do not have any personal competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- COVID Live Coronavirus Statistics—Worldometer n.d. [(accessed on 19 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/
-
- COVID-19 Dynamic Dashboard for Bangladesh. [(accessed on 19 January 2022)]. Available online: https://dghs-dashboard.com/pages/covid19.php.
-
- Ma Q., Liu J., Liu Q., Kang L., Liu R., Jing W., Wu Y., Liu M. Global percentage of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections among the tested population and individuals with confirmed COVID-19 diagnosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open. 2021;4:e2137257. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.37257. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eis-Hübinger A.M., Hönemann M., Wenzel J.J., Berger A., Widera M., Schmidt B., Aldabbagh S., Marx B., Streeck H., Ciesek S., et al. Ad hoc laboratory-based surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 by real-time RT-PCR using minipools of RNA prepared from routine respiratory samples. J. Clin. Virol. 2020;127:104381. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

