Solitary Extrapleural Fibrous Tumor in Salivary Glands: Our Experience-Case Series and Literature Review
- PMID: 36359531
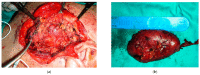
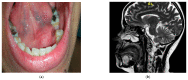
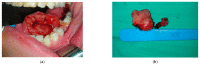
- PMCID: PMC9688987
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12112688
Solitary Extrapleural Fibrous Tumor in Salivary Glands: Our Experience-Case Series and Literature Review
Abstract
(1) Background: Extrapleural solitary fibrous tumors (ESFTs) are rare oncological entities occurring in the head and neck, and even more so in the salivary glands. The clinical presentation and histologic features are usually unspecific, resulting in frequent misclassification. As an unusual tumor, ESTFs have an unpredictable clinical behavior. (2) Methods: We present two clinical cases referred to our Maxillofacial Surgery Unit for the onset of a symptomless mass involving, in one case, the parotid gland, and in the other case, the sublingual gland. (3) Results: Solitary fibrous tumors could be considered as neoplasms with intermediate biological behavior that are not entirely predictable on the basis of morphological features, as these are mostly still unknown. However, a few histologic, immunohistochemical, and imaging features, such as a hypodense signal at the T1 sequence in an MRI, or positivity for CD34, bcl2, and CD99, and the NAB2-STATS6 fusion gene, could be useful for an early differential diagnosis of ESTFs. (4) Conclusions: All patients were alive at follow-up with no evidence of disease. Surgical management should always be considered as the first choice for oncological radicality, and clinical behavior should always be defined with the help of the study of radiological and anatomopathological features.
Keywords: benign tumors; malignancies; parotid gland; salivary gland; solitary extrapleural fibrous tumor; solitary extrapleural fibrous tumor of the head and the neck; sublingual gland; submandibular gland.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Parotid gland solitary fibrous tumor: a case report and clinicopathologic review of 22 cases from the literature.Head Neck Pathol. 2012 Mar;6(1):21-31. doi: 10.1007/s12105-011-0305-8. Epub 2011 Oct 16. Head Neck Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22002440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A solitary fibrous tumor of the parotid gland: Case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Oct;111:108855. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108855. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37742355 Free PMC article.
-
Extrapleural solitary fibrous tumor: A distinct entity from pleural solitary fibrous tumor. An update on clinical, molecular and diagnostic features.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018 Jun;34:142-150. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2018.01.004. Epub 2018 Apr 9. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29660566 Review.
-
Extrapleural Superficial Solitary Fibrous Tumor on the Posterior Shoulder: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Eplasty. 2018 Oct 11;18:e31. eCollection 2018. Eplasty. 2018. PMID: 30455781 Free PMC article.
-
Parotid gland solitary fibrous tumor with mandibular bone destruction and aggressive behavior.J Clin Exp Dent. 2014 Jul 1;6(3):e299-302. doi: 10.4317/jced.51256. eCollection 2014 Jul. J Clin Exp Dent. 2014. PMID: 25136435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klemperer P., Rabin C.B. Primary neoplasm of the pleura: A report of 5 cases. Arch. Pathol. 1931;11:28.
-
- Iorio B., Ronchi A., Montella M., Cozzolino I., De Luca R., Rusciano M., Tartaro G., Colella G., Franco R. Malignant extrapleural solitary fibrous tumor arising in the sublingual gland: A case report and review of literature. Oral Oncol. 2019;90:141–144. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.12.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

