A Computerized Analysis with Machine Learning Techniques for the Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease: Past Studies and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 36359550
- PMCID: PMC9689408
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12112708
A Computerized Analysis with Machine Learning Techniques for the Diagnosis of Parkinson's Disease: Past Studies and Future Perspectives
Abstract
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease of the brain that causes motor symptoms including slower movement, rigidity, tremor, and imbalance in addition to other problems like Alzheimer's disease (AD), psychiatric problems, insomnia, anxiety, and sensory abnormalities. Techniques including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL) have been established for the classification of PD and normal controls (NC) with similar therapeutic appearances in order to address these problems and improve the diagnostic procedure for PD. In this article, we examine a literature survey of research articles published up to September 2022 in order to present an in-depth analysis of the use of datasets, various modalities, experimental setups, and architectures that have been applied in the diagnosis of subjective disease. This analysis includes a total of 217 research publications with a list of the various datasets, methodologies, and features. These findings suggest that ML/DL methods and novel biomarkers hold promising results for application in medical decision-making, leading to a more methodical and thorough detection of PD. Finally, we highlight the challenges and provide appropriate recommendations on selecting approaches that might be used for subgrouping and connection analysis with structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI), DaTSCAN, and single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT) data for future Parkinson's research.
Keywords: MRI; Parkinson’s disease; artificial neural network; deep learning; diagnosis; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

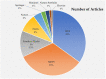
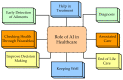
Similar articles
-
A survey of detection of Parkinson's disease using artificial intelligence models with multiple modalities and various data preprocessing techniques.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Oct 28;13:388. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1777_23. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 39703622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imperative Role of Machine Learning Algorithm for Detection of Parkinson's Disease: Review, Challenges and Recommendations.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Aug 19;12(8):2003. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12082003. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of machine learning and deep learning for Parkinson's disease detection.Discov Artif Intell. 2025;5(1):24. doi: 10.1007/s44163-025-00241-9. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Discov Artif Intell. 2025. PMID: 40092968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on computational methods for the detection and classification of Parkinson's Disease.Comput Biol Med. 2025 Mar;187:109767. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2025.109767. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Comput Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 39938340 Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in Parkinson's disease: Early detection and diagnostic advancements.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Aug;99:102410. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102410. Epub 2024 Jul 5. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38972602 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning and wearable sensors for automated Parkinson's disease diagnosis aid: a systematic review.J Neurol. 2024 Oct;271(10):6452-6470. doi: 10.1007/s00415-024-12611-x. Epub 2024 Aug 14. J Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39143345
-
Balance assessment in selected stages of Parkinson's disease using trend change analysis.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023 Aug 2;20(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s12984-023-01229-1. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37528430 Free PMC article.
-
Incorporating label uncertainty during the training of convolutional neural networks improves performance for the discrimination between certain and inconclusive cases in dopamine transporter SPECT.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025 Mar;52(4):1535-1548. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06988-0. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39592475 Free PMC article.
-
Motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease: critical markers for early AI-assisted diagnosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Jul 18;17:1602426. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1602426. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40756325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arias-Vergara T., Vásquez-Correa J.C., Orozco-Arroyave J.R. Parkinson’s Disease and Aging: Analysis of Their Effect in Phonation and Articulation of Speech. Cogn. Comput. 2017;9:731–748. doi: 10.1007/s12559-017-9497-x. - DOI
-
- De Rijk M.D., Launer L.J., Berger K., Breteler M.M., Dartigues J.F., Baldereschi M., Fratiglioni L., Lobo A., Martinez-Lage J., Trenkwalder C., et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in Europe: A collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology. 2000;54((Suppl. 5)):S21–S23. - PubMed
-
- Cantürk İ., Karabiber F. A machine learning system for the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease from speech signals and its application to multiple speech signal types. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016;41:5049–5059. doi: 10.1007/s13369-016-2206-3. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

