Prognostic Model of COVID-19 Severity and Survival among Hospitalized Patients Using Machine Learning Techniques
- PMID: 36359571
- PMCID: PMC9689804
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12112728
Prognostic Model of COVID-19 Severity and Survival among Hospitalized Patients Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract
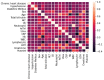
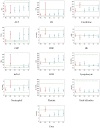
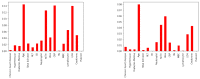
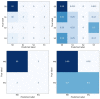
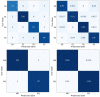
We conducted a statistical study and developed a machine learning model to triage COVID-19 patients affected during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic in Hong Kong based on their medical records and test results (features) collected during their hospitalization. The correlation between the values of these features is studied against discharge status and disease severity as a preliminary step to identify those features with a more pronounced effect on the patient outcome. Once identified, they constitute the inputs of four machine learning models, Decision Tree, Random Forest, Gradient and RUSBoosting, which predict both the Mortality and Severity associated with the disease. We test the accuracy of the models when the number of input features is varied, demonstrating their stability; i.e., the models are already highly predictive when run over a core set of (6) features. We show that Random Forest and Gradient Boosting classifiers are highly accurate in predicting patients' Mortality (average accuracy ∼99%) as well as categorize patients (average accuracy ∼91%) into four distinct risk classes (Severity of COVID-19 infection). Our methodical and broad approach combines statistical insights with various machine learning models, which paves the way forward in the AI-assisted triage and prognosis of COVID-19 cases, which is potentially generalizable to other seasonal flus.
Keywords: COVID-19; machine learning; triage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Organization COVID-19 Dashboard. 2020. [(accessed on 1 April 2022)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Symptoms of COVID-19. [(accessed on 1 April 2022)];2021 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html.
-
- Yan L., Zhang H.T., Xiao Y., Wang M., Guo Y., Sun C., Tang X., Jing L., Zhang M., Yuan Y., et al. An interpretable mortality prediction model for COVID-19 patients. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2020;2:283–288. doi: 10.1038/s42256-020-0180-7. - DOI
-
- Yan L., Zhang H.T., Xiao Y., Wang M., Sun C., Liang J., Li S., Zhang M., Guo Y., Xiao Y., et al. Prediction of criticality in patients with severe COVID-19 infection using three clinical features: A machine learning-based prognostic model with clinical data in Wuhan. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.02.27.20028027. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

