Middle-Inner Macular Layers Dysfunction in a Case of Stellate Foveomacular Retinoschisis Detected by Abnormal Multifocal Photopic Negative Response Recordings
- PMID: 36359596
- PMCID: PMC9689507
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12112753
Middle-Inner Macular Layers Dysfunction in a Case of Stellate Foveomacular Retinoschisis Detected by Abnormal Multifocal Photopic Negative Response Recordings
Abstract
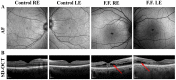
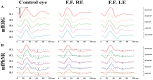
We describe the macular morpho-functional assessment of a 65-year-old man affected by stellate nonhereditary idiopathic foveomacular retinoschisis (SNIFR), studied by visual field, SD-OCT, autofluorescence, full-field electroretinogram (ffERG), multifocal electroretinogram (mfERG) and multifocal Photopic Negative Response (mfPhNR) recordings. The typical presentation consists of the foveal appearance of radial cartwheel pattern for the splitting of the retinal layers at the level of the Henle fiber layer (HFL) and the outer plexiform layer (OPL), perfectly seen by Spectral Domain-Optical Coherence Tomography (SD-OCT). Despite a normal function of the outer retina of the peripheral and central retina evaluated by ffERG and mfERG respectively, we observed a reduced function of the retinal elements involved in the retinoschisis by recording mfPhNR that assesses mainly inner retina function (retinal ganglion cells and their axons). Therefore, it is likely that the observed impaired mfPhNR responses reflect the signaling defects derived from the delaminated middle retina and transmitted to the innermost retinal layers.
Keywords: PhNR; SNIFR; electroretinogram; inner retina; retinoschisis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Montano M., Alfaro D.V., Quiroz-Reyes M.A., Lima-Gómez V., Bonilla L.A., Chew-Bonilla A., Monares-Zepeda G. Stellate unilateral nonhereditary idiopathic foveomacular retinoschisis: A Multimodal imaging analysis and case report. Retin. Cases Brief Rep. 2022;16:439–443. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000001001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

