A Resilience Related Glial-Neurovascular Network Is Transcriptionally Activated after Chronic Social Defeat in Male Mice
- PMID: 36359800
- PMCID: PMC9655779
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11213405
A Resilience Related Glial-Neurovascular Network Is Transcriptionally Activated after Chronic Social Defeat in Male Mice
Abstract
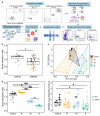
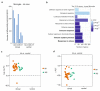
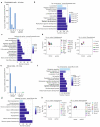
Upon chronic stress, a fraction of individuals shows stress resilience, which can prevent long-term mental dysfunction. The underlying molecular mechanisms are complex and have not yet been fully understood. In this study, we performed a data-driven behavioural stratification together with single-cell transcriptomics of the hippocampus in a mouse model of chronic social defeat stress. Our work revealed that in a sub-group exhibiting molecular responses upon chronic stress, the dorsal hippocampus is particularly involved in neuroimmune responses, angiogenesis, myelination, and neurogenesis, thereby enabling brain restoration and homeostasis after chronic stress. Based on these molecular insights, we applied rapamycin after the stress as a proof-of-concept pharmacological intervention and were able to substantially increase stress resilience. Our findings serve as a data resource and can open new avenues for further understanding of molecular processes underlying stress response and for targeted interventions supporting resilience.
Keywords: cell-cell interaction; glial cells; hippocampus; neuroimmune pathways; neurovascular system; single-cell RNA-seq; stress resilience.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Santomauro D.F., Mantilla Herrera A.M., Shadid J., Zheng P., Ashbaugh C., Pigott D.M., Abbafati C., Adolph C., Amlag J.O., Aravkin A.Y., et al. Global Prevalence and Burden of Depressive and Anxiety Disorders in 204 Countries and Territories in 2020 Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Lancet. 2021;398:1700–1712. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02143-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

