Effective, Long-Term, Neutrophil Depletion Using a Murinized Anti-Ly-6G 1A8 Antibody
- PMID: 36359801
- PMCID: PMC9656769
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11213406
Effective, Long-Term, Neutrophil Depletion Using a Murinized Anti-Ly-6G 1A8 Antibody
Abstract
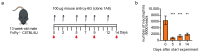
Neutrophils are crucial innate immune cells but also play key roles in various diseases, such as cancer, where they can perform both pro- and anti-tumorigenic functions. To study the function of neutrophils in vivo, these cells are often depleted using Ly-6G or Gr-1 depleting antibodies or genetic "knockout" models. However, these methods have several limitations, being only partially effective, effective for a short term, and lacking specificity or the ability to conditionally deplete neutrophils. Here, we describe the use of a novel murinized Ly-6G (1A8) antibody. The murinized Ly-6G antibody is of the mouse IgG2a isotype, which is the only isotype that can bind all murine Fcγ receptors and C1q and is, therefore, able to activate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), antibody-dependent phagocytosis (ADCP) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) pathways. We show that this mouse-Ly-6G antibody shows efficient, long-term, and near-complete (>90%) neutrophil depletion in the peripheral blood of C57Bl6/J, Balb/c, NXG and SCID mice for up to at least four weeks, using a standardized neutrophil depletion strategy. In addition, we show that neutrophils are efficiently depleted in the blood and tumor tissue of IMR32 tumor-bearing SCID mice, analyzed six weeks after the start of the treatment.
Keywords: cancer; immunotherapy; in vivo neutrophil targeting; neutrophil depletion; neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
J.H.W.L. is co-founder of TigaTx B.V.
Figures



References
-
- Musiani P., Allione A., Modica A., Lollini P.L., Giovarelli M., Cavallo F., Belardelli F., Forni G., Modesti A. Role of neutrophils and lymphocytes in inhibition of a mouse mammary adenocarcinoma engineered to release IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-10, IFN-alpha, IFN-gamma, and TNF-alpha. Lab. Investig. 1996;74:146–157. - PubMed
-
- Schmielau J., Finn O.J. Activated granulocytes and granulocyte-derived hydrogen peroxide are the underlying mechanism of suppression of t-cell function in advanced cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2001;61:4756–4760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

