Assaying Microglia Functions In Vitro
- PMID: 36359810
- PMCID: PMC9654693
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11213414
Assaying Microglia Functions In Vitro
Abstract
Microglia, the main immune modulators of the central nervous system, have key roles in both the developing and adult brain. These functions include shaping healthy neuronal networks, carrying out immune surveillance, mediating inflammatory responses, and disposing of unwanted material. A wide variety of pathological conditions present with microglia dysregulation, highlighting the importance of these cells in both normal brain function and disease. Studies into microglial function in the context of both health and disease thus have the potential to provide tremendous insight across a broad range of research areas. In vitro culture of microglia, using primary cells, cell lines, or induced pluripotent stem cell derived microglia, allows researchers to generate reproducible, robust, and quantifiable data regarding microglia function. A broad range of assays have been successfully developed and optimised for characterizing microglial morphology, mediation of inflammation, endocytosis, phagocytosis, chemotaxis and random motility, and mediation of immunometabolism. This review describes the main functions of microglia, compares existing protocols for measuring these functions in vitro, and highlights common pitfalls and future areas for development. We aim to provide a comprehensive methodological guide for researchers planning to characterise microglial functions within a range of contexts and in vitro models.
Keywords: chemotaxis; endocytosis; functional assays; iPSC; immunometabolism; in vitro; inflammation; microglia; motility; phagocytosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
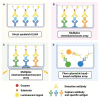
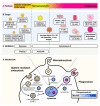

References
-
- Menassa D.A., Muntslag T.A.O., Martin-Estebané M., Barry-Carroll L., Chapman M.A., Adorjan I., Tyler T., Turnbull B., Rose-Zerilli M.J.J., Nicoll J.A.R., et al. The spatiotemporal dynamics of microglia across the human lifespan. Dev. Cell. 2022;57:2127–2139.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2022.07.015. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

