Host Response of Human Epidermis to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Infection and Synthetic Antibiofilm Peptide Treatment
- PMID: 36359854
- PMCID: PMC9657051
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11213459
Host Response of Human Epidermis to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Infection and Synthetic Antibiofilm Peptide Treatment
Abstract
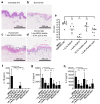
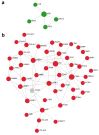
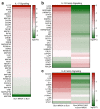
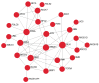
Bacterial biofilm infections associated with wounded skin are prevalent, recalcitrant, and in urgent need of treatments. Additionally, host responses in the skin to biofilm infections are not well understood. Here we employed a human organoid skin model to explore the transcriptomic changes of thermally-injured epidermis to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) biofilm colonization. MRSA biofilm impaired skin barrier function, enhanced extracellular matrix remodelling, elicited inflammatory responses including IL-17, IL-12 family and IL-6 family interleukin signalling, and modulated skin metabolism. Synthetic antibiofilm peptide DJK-5 effectively diminished MRSA biofilm and associated skin inflammation in wounded human ex vivo skin. In the epidermis, DJK-5 shifted the overall skin transcriptome towards homeostasis including modulating the biofilm induced inflammatory response, promoting the skin DNA repair function, and downregulating MRSA invasion of thermally damaged skin. These data clarified the underlying immunopathogenesis of biofilm infections and revealed the intrinsic promise of synthetic peptides in reducing inflammation and biofilm infections.
Keywords: DNA repair; RNA-Seq transcriptomic analysis; biofilm immunopathogenesis; extracellular matrix remodeling; host defense peptide; human skin; inflammation; innate immune response; skin barrier function.
Conflict of interest statement
E.F.H. and R.E.W.H. have invented and filed for patent protection of the antibiofilm peptides described in this study. This patent has been assigned to their employer, the University of British Columbia, and has been licensed to ABT Innovations Inc., in which R.E.W.H. has an ownership position. ABT Innovations Inc. is a subsidiary of ASEP Medical Holdings Inc. E.F.H. is employed by ASEP and receives salary while R.E.W.H. holds an executive position and is on the Board of ASEP. The rest of the authors B.W., T.M.B., R.F., and N.A. declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Antimicrobial Resistance. [(accessed on 5 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance.
-
- WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. [(accessed on 5 September 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

