Integration of O-GlcNAc into Stress Response Pathways
- PMID: 36359905
- PMCID: PMC9654274
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11213509
Integration of O-GlcNAc into Stress Response Pathways
Abstract
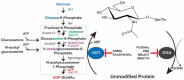
The modification of nuclear, mitochondrial, and cytosolic proteins by O-linked βN-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) has emerged as a dynamic and essential post-translational modification of mammalian proteins. O-GlcNAc is cycled on and off over 5000 proteins in response to diverse stimuli impacting protein function and, in turn, epigenetics and transcription, translation and proteostasis, metabolism, cell structure, and signal transduction. Environmental and physiological injury lead to complex changes in O-GlcNAcylation that impact cell and tissue survival in models of heat shock, osmotic stress, oxidative stress, and hypoxia/reoxygenation injury, as well as ischemic reperfusion injury. Numerous mechanisms that appear to underpin O-GlcNAc-mediated survival include changes in chaperone levels, impacts on the unfolded protein response and integrated stress response, improvements in mitochondrial function, and reduced protein aggregation. Here, we discuss the points at which O-GlcNAc is integrated into the cellular stress response, focusing on the roles it plays in the cardiovascular system and in neurodegeneration.
Keywords: O-GlcNAc; chaperone; glycosylation; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

