Effect of Autochthonous Lactic Acid Bacteria-Enhanced Fermentation on the Quality of Suancai
- PMID: 36359923
- PMCID: PMC9657813
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11213310
Effect of Autochthonous Lactic Acid Bacteria-Enhanced Fermentation on the Quality of Suancai
Abstract
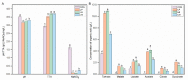
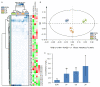
The lactic acid bacteria (LABs) used for fermentation have an extremely vital impact on the quality of Suancai, a fermented vegetable. The bacterial diversity and metabolites of inoculated Suancai with LABs, including Lactiplantibacillus plantarum (Lb. plantarum), Levilactabacillus brevis (Lb. brevis), and Leuconostoc mesenteroides (Leu. mesenteroides), were investigated. The inoculation of LABs significantly decreased the pH and the content of nitrite. The Suancai inoculated with LABs had a higher content of the total titratable acidity (TTA) and organic acids than spontaneous fermentation. The LABs inoculation significantly influenced the bacterial community structures, which directly or indirectly caused changes of metabolites. The bacterial community profiles of Suancai inoculated with Lb. plantarum were more similar to spontaneous fermentation. The inoculation of Lb. plantarum, Lb. brevis, and Leu. mesenteroides could increase its abundance in Suancai. Whatever the species inoculated, Lb. plantarum was always the predominant bacterium in Suancai after fermentation. The inoculated LABs were positively correlated with most volatile compounds and amino acids. The inoculated LABs significantly improved the volatile compounds and amino acid content of Suancai. This study could contribute to understanding the function of starters in Suancai fermentation and promote the selection of applicable starters for high-quality Suancai production.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum; Leuconostoc mesenteroides; Levilactabacillus brevis; Suancai; inoculated fermentation; lactic acid bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improving the quality of Suancai by inoculating with Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus pentosaceus.Food Res Int. 2021 Oct;148:110581. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110581. Epub 2021 Jul 1. Food Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34507728
-
Microbial communities and metabolite profiles during the fermentation of Chinese Dongbei suancai with Chinese baijiu as supplementary material.J Sci Food Agric. 2023 May;103(7):3521-3530. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12510. Epub 2023 Mar 3. J Sci Food Agric. 2023. PMID: 36799142
-
Study of bacterial community succession and reconstruction of the core lactic acid bacteria to enhance the flavor of paocai.Int J Food Microbiol. 2022 Aug 16;375:109702. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109702. Epub 2022 May 6. Int J Food Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35635993
-
Insight into the autochthonous lactic acid bacteria as starter culture for improving the quality of Sichuan radish paocai: Changes in microbial diversity and metabolic profiles.Int J Food Microbiol. 2024 Dec 2;425:110877. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2024.110877. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Int J Food Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39173287
-
Evaluation and mechanism of the antioxidant activity of lactic acid bacteria.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025 Jun 7. doi: 10.1007/s12223-025-01277-1. Online ahead of print. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025. PMID: 40481970 Review.
Cited by
-
Highlighting Lactic Acid Bacteria in Beverages: Diversity, Fermentation, Challenges, and Future Perspectives.Foods. 2025 Jun 10;14(12):2043. doi: 10.3390/foods14122043. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40565651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect on Arabica Coffee Flavor Quality of Enhanced Fermentation With Pichia membranifaciens Through Change Microbial Communities and Chemical Compounds.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Jun 28;13(7):e70512. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70512. eCollection 2025 Jul. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40585504 Free PMC article.
-
Bioprotective Potential of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Pickled Pepper Rabbit Meat During Refrigerated Storage.Foods. 2025 Aug 21;14(16):2918. doi: 10.3390/foods14162918. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40870829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xiao Y., Huang T., Huang C., Jim H., Peng Z., Xie M., Xiong T. The microbial communities and flavour compounds of Jiangxi yancai, Sichuan paocai and Dongbei Suancai: Three major types of traditional Chinese fermented vegetables. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020;121:108865. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108865. - DOI
-
- Satora P., Skotniczny M., Strnad S., Piechowicz W. Chemical composition and sensory quality of sauerkraut produced from different cabbage varieties. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021;136:110325. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110325. - DOI
-
- He Z., Wang X., Chen H., Lin X., Ji C., Li S., Liang H. Effects of different temperatures on bacterial diversity and volatile flavor compounds during the fermentation of Suancai, a traditional fermented vegetable food from northeastern China. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020;118:108773. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108773. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

