Heuristic Pairwise Alignment in Database Environments
- PMID: 36360242
- PMCID: PMC9690874
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13112005
Heuristic Pairwise Alignment in Database Environments
Abstract
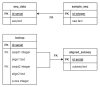
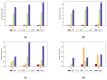
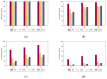
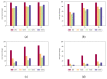
Biological data have gained wider recognition during the last few years, although managing and processing these data in an efficient way remains a challenge in many areas. Increasingly, more DNA sequence databases can be accessed; however, most algorithms on these sequences are performed outside of the database with different bioinformatics software. In this article, we propose a novel approach for the comparative analysis of sequences, thereby defining heuristic pairwise alignment inside the database environment. This method takes advantage of the benefits provided by the database management system and presents a way to exploit similarities in data sets to quicken the alignment algorithm. We work with the column-oriented MonetDB, and we further discuss the key benefits of this database system in relation to our proposed heuristic approach.
Keywords: bioinformatics; database systems; pairwise alignment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




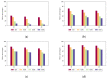
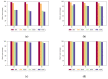
References
-
- Can T. miRNomics: MicroRNA Biology and Computational Analysis. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2014. Introduction to bioinformatics; pp. 51–71.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

