Translational Regulation by eIFs and RNA Modifications in Cancer
- PMID: 36360287
- PMCID: PMC9690228
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13112050
Translational Regulation by eIFs and RNA Modifications in Cancer
Abstract
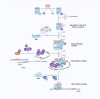
Translation is a fundamental process in all living organisms that involves the decoding of genetic information in mRNA by ribosomes and translation factors. The dysregulation of mRNA translation is a common feature of tumorigenesis. Protein expression reflects the total outcome of multiple regulatory mechanisms that change the metabolism of mRNA pathways from synthesis to degradation. Accumulated evidence has clarified the role of an increasing amount of mRNA modifications at each phase of the pathway, resulting in translational output. Translation machinery is directly affected by mRNA modifications, influencing translation initiation, elongation, and termination or altering mRNA abundance and subcellular localization. In this review, we focus on the translation initiation factors associated with cancer as well as several important RNA modifications, for which we describe their association with cancer.
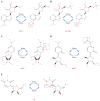
Keywords: 2′-O-dimethyladenosine (m6Am); 5-methylcytosine (m5C); N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C); N6; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); RNA modification; pseudouridine (Ψ); translation initiation factor; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sequencing methods and functional decoding of mRNA modifications.Fundam Res. 2023 Jun 1;3(5):738-748. doi: 10.1016/j.fmre.2023.05.010. eCollection 2023 Sep. Fundam Res. 2023. PMID: 38933299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional interplay within the epitranscriptome: Reality or fiction?Bioessays. 2022 Feb;44(2):e2100174. doi: 10.1002/bies.202100174. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Bioessays. 2022. PMID: 34873719 Review.
-
[Progress in epigenetic modification of mRNA and the function of m6A modification].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2019 May 25;35(5):775-783. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.180416. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2019. PMID: 31222996 Review. Chinese.
-
Epitranscriptomic Regulations in the Heart.Physiol Res. 2024 Apr 18;73(Suppl 1):S185-S198. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935265. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Physiol Res. 2024. PMID: 38634649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Epitranscriptome in Translation Regulation.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 Aug 1;11(8):a032623. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a032623. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 30037968 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the Anticancer Mechanism of OR3 Pigment from Streptomyces coelicolor JUACT03 Against the Human Hepatoma Cell Line Using a Proteomic Approach.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):1061-1077. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01258-0. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38578403
-
Exosomal insights into ovarian cancer stem cells: revealing the molecular hubs.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Jan 31;18(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01597-3. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 39891297 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles and clinical perspectives of RNA methylation in cancer.MedComm (2020). 2024 May 7;5(5):e559. doi: 10.1002/mco2.559. eCollection 2024 May. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38721006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the potential role of RNA N4-acetylcytidine in cancer progression.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 17;22(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01417-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38233930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BLF1 Affects ATP Hydrolysis Catalyzed by Native and Mutated eIF4A1 and eIF4A2 Proteins.Toxins (Basel). 2025 May 7;17(5):232. doi: 10.3390/toxins17050232. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40423315 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

