From Processivity to Genome Maintenance: The Many Roles of Sliding Clamps
- PMID: 36360296
- PMCID: PMC9690074
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13112058
From Processivity to Genome Maintenance: The Many Roles of Sliding Clamps
Abstract
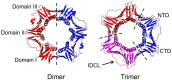
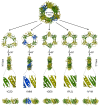
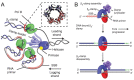
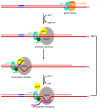
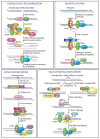
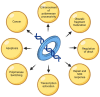
Sliding clamps play a pivotal role in the process of replication by increasing the processivity of the replicative polymerase. They also serve as an interacting platform for a plethora of other proteins, which have an important role in other DNA metabolic processes, including DNA repair. In other words, clamps have evolved, as has been correctly referred to, into a mobile "tool-belt" on the DNA, and provide a platform for several proteins that are involved in maintaining genome integrity. Because of the central role played by the sliding clamp in various processes, its study becomes essential and relevant in understanding these processes and exploring the protein as an important drug target. In this review, we provide an updated report on the functioning, interactions, and moonlighting roles of the sliding clamps in various organisms and its utilization as a drug target.
Keywords: dimer; moonlight role; processivity factor; sliding clamp; trimer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A proposal: Evolution of PCNA's role as a marker of newly replicated DNA.DNA Repair (Amst). 2015 May;29:4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2015.01.015. Epub 2015 Feb 9. DNA Repair (Amst). 2015. PMID: 25704660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loading clamps for DNA replication and repair.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 May 1;8(5):570-8. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2008.12.014. Epub 2009 Feb 11. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 19213612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clamp loading, unloading and intrinsic stability of the PCNA, beta and gp45 sliding clamps of human, E. coli and T4 replicases.Genes Cells. 1996 Jan;1(1):101-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.1996.07007.x. Genes Cells. 1996. PMID: 9078370
-
Evolution and origin of sliding clamp in bacteria, archaea and eukarya.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 11;16(8):e0241093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241093. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34379636 Free PMC article.
-
Replication clamps and clamp loaders.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013 Apr 1;5(4):a010165. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a010165. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013. PMID: 23545418 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peptide-Based Covalent Inhibitors Bearing Mild Electrophiles to Target a Conserved His Residue of the Bacterial Sliding Clamp.JACS Au. 2024 Jan 25;4(2):432-440. doi: 10.1021/jacsau.3c00572. eCollection 2024 Feb 26. JACS Au. 2024. PMID: 38425897 Free PMC article.
-
Non-lytic spread of poliovirus requires the nonstructural protein 3CD.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 19:2024.10.18.619132. doi: 10.1101/2024.10.18.619132. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):e0327624. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03276-24. PMID: 39464037 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Subtractive genomics study of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae reveals repurposable drug candidate for the treatment of bacterial leaf blight in rice.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;22(1):100353. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2024.100353. Epub 2024 Jan 23. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38494267 Free PMC article.
-
Non-lytic spread of poliovirus requires the nonstructural protein 3CD.mBio. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):e0327624. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03276-24. Epub 2024 Dec 12. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39665531 Free PMC article.
-
The bacterial DNA sliding clamp, β-clamp: structure, interactions, dynamics and drug discovery.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 May 30;81(1):245. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05252-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38814467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maga G. Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. DNA Polymerases.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

