Advancements in Dentistry with Artificial Intelligence: Current Clinical Applications and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 36360529
- PMCID: PMC9690084
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10112188
Advancements in Dentistry with Artificial Intelligence: Current Clinical Applications and Future Perspectives
Abstract
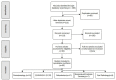
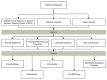
Artificial intelligence has been widely used in the field of dentistry in recent years. The present study highlights current advances and limitations in integrating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in subfields of dentistry including periodontology, endodontics, orthodontics, restorative dentistry, and oral pathology. This article aims to provide a systematic review of current clinical applications of artificial intelligence within different fields of dentistry. The preferred reporting items for systematic reviews (PRISMA) statement was used as a formal guideline for data collection. Data was obtained from research studies for 2009-2022. The analysis included a total of 55 papers from Google Scholar, IEEE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results show that artificial intelligence has the potential to improve dental care, disease diagnosis and prognosis, treatment planning, and risk assessment. Finally, this study highlights the limitations of the analyzed studies and provides future directions to improve dental care.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; clinical applications; deep learning; dentistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contemporary Role and Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Dentistry.F1000Res. 2023 Sep 20;12:1179. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.140204.1. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2023. PMID: 37942018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence in dentistry: Exploring emerging applications and future prospects.J Dent. 2025 Apr;155:105648. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2025.105648. Epub 2025 Feb 22. J Dent. 2025. PMID: 39993553 Review.
-
Applications and Perspectives of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and "Dentronics" in Dentistry: A Literature Review.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2023 Feb 27;13(1):1-8. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_35_22. eCollection 2023 Jan-Feb. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2023. PMID: 37153930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications, functions, and accuracy of artificial intelligence in restorative dentistry: A literature review.J Esthet Restor Dent. 2023 Sep;35(6):842-859. doi: 10.1111/jerd.13079. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Esthet Restor Dent. 2023. PMID: 37522291 Review.
-
Where Is the Artificial Intelligence Applied in Dentistry? Systematic Review and Literature Analysis.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 8;10(7):1269. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10071269. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885796 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence in forensic medicine and forensic dentistry.J Forensic Odontostomatol. 2023 Aug 27;41(2):30-41. J Forensic Odontostomatol. 2023. PMID: 37634174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fully automated deep learning approach to dental development assessment in panoramic radiographs.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Apr 6;24(1):426. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04160-6. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38582843 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic performance of artificial intelligence using cone-beam computed tomography imaging of the oral and maxillofacial region: A scoping review and meta-analysis.Imaging Sci Dent. 2023 Jun;53(2):101-108. doi: 10.5624/isd.20220224. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Imaging Sci Dent. 2023. PMID: 37405196 Free PMC article.
-
A visualization system for intelligent diagnosis and statistical analysis of oral diseases based on panoramic radiography.Sci Rep. 2025 May 25;15(1):18222. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01733-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40414918 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the accuracy of CHATGPT models in answering multiple-choice questions on oral and maxillofacial pathologies and oral radiology.Digit Health. 2025 Jul 8;11:20552076251355847. doi: 10.1177/20552076251355847. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40656850 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Haykin S. Neural Networks and Learning Machines, 3/E. Pearson Education India; Noida, India: 2009.
-
- Jain A.K., Mao J., Mohiuddin K.M. Artificial neural networks: A tutorial. Computer. 1996;29:31–44. doi: 10.1109/2.485891. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources