Effectiveness of Educational Interventions to Increase Skills in Evidence-Based Practice among Nurses: The EDITcare Systematic Review
- PMID: 36360544
- PMCID: PMC9691114
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10112204
Effectiveness of Educational Interventions to Increase Skills in Evidence-Based Practice among Nurses: The EDITcare Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Using evidence-based practice (EBP) improves the implementation of safe, high-quality healthcare for patients, reduces avoidable costs, and plays a crucial role in bridging knowledge-action gaps and reducing health inequities. EBP combines the best available evidence in the relevant literature with patient preferences and values and healthcare professionals' (HCPs) expertise.
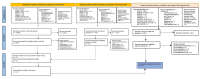
Methods: Systematic searches of ten bibliographic databases, unpublished works, and the Grey Literature Report sought studies published up to 30 September 2022.
Results: The 15 studies retained involved 2712 nurses. Three types of effective educational interventions were identified: (1) multifaceted educational strategies incorporating mentoring and tutoring; (2) single educational strategies, often delivered online; and (3) multifaceted educational strategies using the five steps of EBP. Eleven primary outcomes (EBP beliefs, EBP self-efficacy, perceived EBP implementation, EBP competencies, EBP knowledge, EBP skills, EBP attitudes, EBP behaviors, EBP desire, EBP practice, and perceptions of organizational culture and readiness) were assessed using 13 qualitative and quantitative instruments.
Conclusions: Ensuring the successful implementation of EBP requires effective educational strategies. Computer-based learning seems the most cost-effective and efficient strategy, when considering caregivers' characteristics, the clinical field, and educational interventions across the pre-, peri-, and post-implementation processes.
Keywords: beliefs; education; evidence-based practice; implementation; interventions; knowledge; nurses; primary healthcare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder was not involved in protocol design or the plan of analyses, nor will it be involved in the interpretation or publication of the systematic review’s results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evidence-Based Practice Beliefs, Implementation, and Organizational Culture and Readiness for EBP Among Nurses, Midwives, Educators, and Students in the Republic of Ireland.Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2021 Dec;18(6):379-388. doi: 10.1111/wvn.12543. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2021. PMID: 34750977
-
Practicing Healthcare Professionals' Evidence-Based Practice Competencies: An Overview of Systematic Reviews.Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2019 Jun;16(3):176-185. doi: 10.1111/wvn.12363. Epub 2019 May 10. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2019. PMID: 31074582
-
Effectiveness of Educational Interventions to Increase Knowledge of Evidence-Based Practice Among Nurses and Physiotherapists in Primary Health Care: Protocol for a Systematic Review.JMIR Res Protoc. 2020 Nov 2;9(11):e17621. doi: 10.2196/17621. JMIR Res Protoc. 2020. PMID: 33136056 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-informed practice versus evidence-based practice educational interventions for improving knowledge, attitudes, understanding, and behavior toward the application of evidence into practice: A comprehensive systematic review of UG student.Campbell Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 16;18(2):e1233. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1233. eCollection 2022 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36911346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of an Online Educational Module in Improving Evidence-Based Practice Skills of Practicing Registered Nurses.Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2017 Oct;14(5):358-366. doi: 10.1111/wvn.12214. Epub 2017 Mar 7. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs. 2017. PMID: 28267902
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of the Pediatric Nursing Excellence Model on Nurses' Knowledge and Practice in Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery Care: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Children (Basel). 2024 Nov 29;11(12):1457. doi: 10.3390/children11121457. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39767887 Free PMC article.
-
Current Approaches on Nurse-Performed Interventions to Prevent Healthcare-Acquired Infections: An Umbrella Review.Microorganisms. 2025 Feb 19;13(2):463. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020463. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Examining knowledge, attitudes, and implementation of evidence-based practice among nursing students: a multicenter cross-sectional study.BMC Nurs. 2025 Mar 24;24(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12912-025-02963-8. BMC Nurs. 2025. PMID: 40128851 Free PMC article.
-
PICOT questions and search strategies formulation: A novel approach using artificial intelligence automation.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2025 Jan;57(1):5-16. doi: 10.1111/jnu.13036. Epub 2024 Nov 24. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2025. PMID: 39582233 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to implement evidence-informed decision making at the organizational level: a rapid systematic review.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Apr 1;24(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10841-3. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38561796 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources