Effectiveness of Physical Exercise Interventions on Pulmonary Function and Physical Fitness in Children and Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36360546
- PMCID: PMC9690212
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10112205
Effectiveness of Physical Exercise Interventions on Pulmonary Function and Physical Fitness in Children and Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
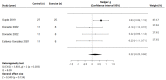
Objective: Physical exercise is associated with several benefits in the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF), associated with a reduction in patient mortality. The aim of this systematic review was to determine the effectiveness of exercise interventions on physical condition and lung function in children and adults with CF to establish the most appropriate type and dose of physical exercise used so far. Methods: The studies included were randomized controlled trials with physical exercise interventions performed with children or adults with CF, analyzing the effects on pulmonary function, cardiorespiratory capacity, and muscle strength. The variables analyzed in at least four studies in the same population (children or adults) with the same measuring test were included in the meta-analysis. Results:Pulmonary function: There were no changes in the forced expiratory volume 1 s, but mouth expiratory/inspiratory pressures were improved in some studies. Physical fitness: In children, the interventions did not manage to improve the VO2peak (SMD = 0.22; 95%CI: -0.25 to 0.68; p = 0.73) but improved muscle strength. In adults, physical exercise interventions based on high-intensity aerobic training showed positive results in the VO2peak, and in some muscle strength outcomes. Conclusions: Exercise interventions in children and adults with CF are effective in improving muscle strength, cardiovascular capacity, and respiratory muscle function. However, they do not achieve improvements in lung function. The most effective programs are those using strength training or cardiovascular high-intensity interval training, although to date there have been few such interventions.
Keywords: cardiorespiratory function; cystic fibrosis; exercise; muscle strength; physical fitness; pulmonary function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is exercise and electrostimulation effective in improving muscle strength and cardiorespiratory fitness in children with cystic fibrosis and mild-to-moderate pulmonary impairment?: Randomized controlled trial.Respir Med. 2022 May;196:106798. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2022.106798. Epub 2022 Mar 1. Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 35306386 Clinical Trial.
-
Respiratory muscle training for cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 17;12(12):CD006112. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006112.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33331663 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training undertaken by people within 12 months of lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 17;6(6):CD009955. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009955.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31204439 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of respiratory and peripheral muscle strength, functional exercise capacity, activities of daily living and physical fitness in patients with cystic fibrosis and healthy subjects.Res Dev Disabil. 2015 Oct-Nov;45-46:147-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2015.07.020. Epub 2015 Aug 1. Res Dev Disabil. 2015. PMID: 26241869
-
Intrahospital weight and aerobic training in children with cystic fibrosis: a randomized controlled trial.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012 Jan;44(1):2-11. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e318228c302. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012. PMID: 21685814 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Effect of Water-Based vs. Land-Based Exercise Intervention (postCOVIDkids) on Exercise Capacity, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Children with Post COVID-19 Condition: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 28;12(19):6244. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196244. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834888 Free PMC article.
-
Move-PCD-a multi-center longitudinal randomized controlled superiority trial on the effect of a 6-month individualized supported physical activity (PA) program on quality of life (QoL) in children, adolescents, and adults with primary ciliary dyskinesia.Trials. 2024 Aug 15;25(1):539. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08379-0. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39148115 Free PMC article.
-
Combined CFTR modulator therapies are linked with anabolic benefits and insulin-sparing in cystic fibrosis-related diabetes.J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2023 Jun 24;33:100320. doi: 10.1016/j.jcte.2023.100320. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Clin Transl Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37448650 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Physical Activity on Clinical Outcomes in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: A Narrative Review.Children (Basel). 2025 Jun 23;12(7):831. doi: 10.3390/children12070831. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen D.H. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and its relation to celiac disease: A clinical and pathologic study. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1938;56:344–399. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1938.01980140114013. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources