Acute Effects of Whole-Body Electromyostimulation during a Single Maximal Strength Training Session
- PMID: 36360629
- PMCID: PMC9657354
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192113753
Acute Effects of Whole-Body Electromyostimulation during a Single Maximal Strength Training Session
Abstract
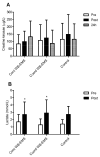
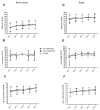
Whole-body electromyostimulation (WB-EMS) training is effective in improving training adaptation. However, WB-EMS may have side effects and contraindications that can lead to excessive muscle damage and physiological impairment. This randomized crossover study aimed to analyze the acute effects of WB-EMS on muscle damage, autonomic modulation and performance during a single maximal strength session in physically active participants. Twenty healthy and physically active participants randomly performed three maximal strength training sessions (90% 1RM) consisting of bench presses and squat exercises, with a continuous stimulus, a coordinated stimulus with concentric and eccentric phases, and without WB-EMS. Data showed no significant differences between the trials for muscle damage (blood creatine kinase levels), lactate blood levels and performance after exercise. Likewise, the heart rate, blood oxygen saturation and the rate of perceived exertion were similar during exercise between trials. The heart rate variability analysis also showed a similar autonomic response among the trials. Training with WB-EMS seemed to be safe at the observed time intervals while offering a stimulus similar to regular training in physically active participants, regardless of the delivery of the electrical stimuli. More studies are needed to assess the effectiveness of WB-EMS in improving exercise adaptations during training programs.
Keywords: WB-EMS; acute effects; creatine kinase; heart rate variability; muscle damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Four Weeks of Static vs. Dynamic Bodyweight Exercises with Whole-Body Electromyostimulation on Jump and Strength Performance: A Two-Armed, Randomized, Controlled Trial.J Sports Sci Med. 2023 Jun 1;22(2):226-234. doi: 10.52082/jssm.2023.226. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2023. PMID: 37293409 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of whole-body electromyostimulation training on upper limb muscles strength and body composition in moderately trained males: A randomized controlled study.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 9;10:982062. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.982062. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36159315 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Whole-Body Electromyostimulation versus Recognized Back-Strengthening Exercise Training on Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain: A Randomized Controlled Study.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Sep 29;2019:5745409. doi: 10.1155/2019/5745409. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31687394 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Side effects of whole-body electro-myo-stimulation.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2019 May;169(7-8):173-180. doi: 10.1007/s10354-018-0655-x. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2019. PMID: 30141113 Review. English.
-
Effects of Whole-Body Electromyostimulation on Strength-, Sprint-, and Jump Performance in Moderately Trained Young Adults: A Mini-Meta-Analysis of Five Homogenous RCTs of Our Work Group.Front Physiol. 2019 Nov 8;10:1336. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01336. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31780950 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of 8-week frequency-specific electrical muscle stimulation combined with resistance exercise training on muscle mass, strength, and body composition in men and women: a feasibility and safety study.PeerJ. 2023 Oct 16;11:e16303. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16303. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37868059 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Babault N., Cometti G., Bernardin M., Pousson M., Chatard J.C. Effects of electromyostimulation training on muscle strength and power of elite rugby players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007;21:431–437. - PubMed
-
- Filipovic A., Kleinoder H., Dormann U., Mester J. Electromyostimulation a systematic review of the effects of different electromyostimulation methods on selected strength parameters in trained and elite athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2012;26:2600–2614. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e31823f2cd1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herrero A.J., Martin J., Martin T., Abadia O., Fernández B., García-López D. Short-term effect of plyometrics and strength training with and without superimposed electrical stimulation on muscle strength and anaerobic performance: A randomized controlled trial. Part II. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010;24:1616–1622. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181d8e84b. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herrero A.J., Martin J., Martin T., Abadia O., Fernández B., García-López D. Short-term effect of strength training with and without superimposed electrical stimulation on muscle strength and anaerobic performance. A randomized controlled trial. Part I. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010;24:1609–1615. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181dc427e. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

