Modeling COVID-19 Transmission Dynamics: A Bibliometric Review
- PMID: 36361019
- PMCID: PMC9655715
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192114143
Modeling COVID-19 Transmission Dynamics: A Bibliometric Review
Abstract
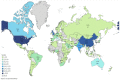
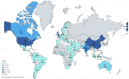
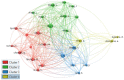
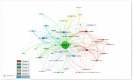
A good amount of research has evolved just in three years in COVID-19 transmission, mortality, vaccination, and some socioeconomic studies. A few bibliometric reviews have already been performed in the literature, especially on the broad theme of COVID-19, without any particular area such as transmission, mortality, or vaccination. This paper fills this gap by conducting a bibliometric review on COVID-19 transmission as the first of its kind. The main aim of this study is to conduct a bibliometric review of the literature in the area of COVID-19 transmission dynamics. We have conducted bibliometric analysis using descriptive and network analysis methods to review the literature in this area using RStudio, Openrefine, VOSviewer, and Tableau. We reviewed 1103 articles published in 2020-2022. The result identified the top authors, top disciplines, research patterns, and hotspots and gave us clear directions for classifying research topics in this area. New research areas are rapidly emerging in this area, which needs constant observation by researchers to combat this global epidemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 transmission; bibliometric review; infectious diseases; public health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- CDC CDC Museum COVID-19 Timeline. [(accessed on 10 October 2022)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/museum/timeline/covid19.html.
-
- Nuno F. IESE Business School Working Paper No. WP-1240-E. 2020. [(accessed on 13 October 2022)]. Economic Effects of Coronavirus Outbreak (COVID-19) on the World Economy. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3557504.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous