Measuring Comprehensive, General Health Literacy in the General Adult Population: The Development and Validation of the HLS19-Q12 Instrument in Seventeen Countries
- PMID: 36361025
- PMCID: PMC9659295
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192114129
Measuring Comprehensive, General Health Literacy in the General Adult Population: The Development and Validation of the HLS19-Q12 Instrument in Seventeen Countries
Abstract
Background: For improving health literacy (HL) by national and international public health policy, measuring population HL by a comprehensive instrument is needed. A short instrument, the HLS19-Q12 based on the HLS-EU-Q47, was developed, translated, applied, and validated in 17 countries in the WHO European Region.
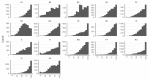
Methods: For factorial validity/dimensionality, Cronbach alphas, confirmatory factor analysis (CFA), Rasch model (RM), and Partial Credit Model (PCM) were used. For discriminant validity, correlation analysis, and for concurrent predictive validity, linear regression analysis were carried out.
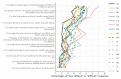
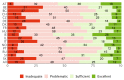
Results: The Cronbach alpha coefficients are above 0.7. The fit indices for the single-factor CFAs indicate a good model fit. Some items show differential item functioning in certain country data sets. The regression analyses demonstrate an association of the HLS19-Q12 score with social determinants and selected consequences of HL. The HLS19-Q12 score correlates sufficiently highly (r ≥ 0.897) with the equivalent score for the HLS19-Q47 long form.
Conclusions: The HLS19-Q12, based on a comprehensive understanding of HL, shows acceptable psychometric and validity characteristics for different languages, country contexts, and methods of data collection, and is suitable for measuring HL in general, national, adult populations. There are also indications for further improvement of the instrument.
Keywords: HLS19; HLS19-Q12; health literacy measurement; instrument development; national adult population; validation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kickbusch I., Pelikan J.M., Apfel F., Tsouros A.D. Health Literacy: The Solid Facts. World Health Organization (WHO) Regional Office for Europe; Copenhagen, Denmark: 2013.
-
- HLS-EU Consortium . Comparative Report on Health Literacy in Eight EU Member States. The European Health Literacy Survey HLS-EU; Wien, Austria: 2012. Second Extended and Revised Version, Date 22 July 2014.
-
- Sørensen K., Pelikan J.M., Röthlin F., Ganahl K., Slonska Z., Doyle G., Fullam J., Kondilis B., Agrafiotis D., Uiters E., et al. Health literacy in Europe: Comparative results of the European health literacy survey (HLS-EU) Eur. J. Public Health. 2015;25:1053–1058. doi: 10.1093/eurpub/ckv043. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- M-POHL . Concept Note. For a WHO Action Network on Measuring Population and Organizational Health Literacy (M-POHL Network) within the European Health Information Initiative (EHII) M-POHL; Vienna, Austria: 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

