Aneurysm Sac Pressure during Branched Endovascular Aneurysm Repair versus Multilayer Flow Modulator Implantation in Patients with Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm
- PMID: 36361444
- PMCID: PMC9655300
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph192114563
Aneurysm Sac Pressure during Branched Endovascular Aneurysm Repair versus Multilayer Flow Modulator Implantation in Patients with Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Abstract
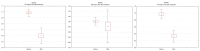
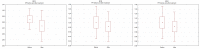
Open thoracoabdominal repair is the gold standard in the TAAA treatment. However, there are endovascular techniques, that sometimes may be an alternative, such as branched endovascular aneurysm repair (BEVAR) or implantation of the multilayer flow modulator (MFM). In this study, we aimed to assess differences in the aneurysm sac pressure (ASP) between patients undergoing BEVAR and MFM implantation. The study included 22 patients with TAAA (14 patients underwent BEVAR, while eight MFM implantation). The pressure sensor wire was placed inside the aneurysm. A measurement of ASP and aortic pressure (AP) was performed during the procedure. The systolic pressure index (SPI), diastolic pressure index (DPI), and pulse pressure index (PPI) were calculated as a quotient of the ASP and AP values. After the procedure, SPI and PPI were lower in the BEVAR group than in the MFM group. During a procedure, a drop in SPI and PPI was noted in patients undergoing BEVAR, while no changes were revealed in the MFM group. This indicates that BEVAR, but not MFM, is associated with a reduction in systolic and pulse pressure in the aneurysm sac in patients with TAAA.
Keywords: aneurysm sac pressure; endovascular aneurysm repair; multilayer flow modulator; thoracoabdominal aneurysm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early mid-term results of the first 103 cases of multilayer flow modulator stent done under indication for use in the management of thoracoabdominal aortic pathology from the independent global MFM registry.J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2014 Feb;55(1):21-32. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino). 2014. PMID: 24356043
-
Multilayer Flow Modulator Treatment of Abdominal and Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysms With Side Branch Coverage: Outcomes From a Prospective Single-Center Moroccan Registry.J Endovasc Ther. 2016 Oct;23(5):773-82. doi: 10.1177/1526602816657087. Epub 2016 Jul 4. J Endovasc Ther. 2016. PMID: 27381934 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm extent on outcomes in patients undergoing fenestrated/branched endovascular aneurysm repair.J Vasc Surg. 2021 Sep;74(3):833-842.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2021.01.062. Epub 2021 Feb 19. J Vasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33617981
-
A clinical review of early outcomes from contemporary flow modulation versus open, fenestrated and branch technologies in the management of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm.Vascular. 2018 Apr;26(2):209-215. doi: 10.1177/1708538117724933. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Vascular. 2018. PMID: 28836901 Review.
-
Duplex ultrasound follow-up after fenestrated and branched endovascular aneurysm repair (FEVAR and BEVAR).Semin Vasc Surg. 2020 Dec;33(3-4):60-64. doi: 10.1053/j.semvascsurg.2020.05.006. Epub 2020 May 23. Semin Vasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 33308597 Review.
References
-
- Verhoeven E.L.G., Zeebregts C.J., Kapma M.R., Tielliu I.F.J., Prins T.R., van den Dungen J.J.A.M. Fenestrated and branched endovascular techniques for thoraco-abdominal aneurysm repair. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005;46:131–140. - PubMed
-
- Verhoeven E.L.G., Tielliu I.F.J., Ferreira M., Zipfel B., Adam D.J. Thoraco-abdominal aortic aneurysm branched repair. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010;51:149–155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

