Molecular Mechanism of Sirtuin 1 Modulation by the AROS Protein
- PMID: 36361557
- PMCID: PMC9654219
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232112764
Molecular Mechanism of Sirtuin 1 Modulation by the AROS Protein
Abstract
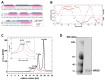
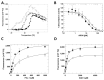
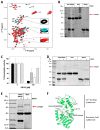
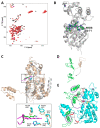
The protein lysine deacylases of the NAD+-dependent Sirtuin family contribute to metabolic regulation, stress responses, and aging processes, and the human Sirtuin isoforms, Sirt1-7, are considered drug targets for aging-related diseases. The nuclear isoform Sirt1 deacetylates histones and transcription factors to regulate, e.g., metabolic adaptations and circadian mechanisms, and it is used as a therapeutic target for Huntington's disease and psoriasis. Sirt1 is regulated through a multitude of mechanisms, including the interaction with regulatory proteins such as the inhibitors Tat and Dbc1 or the activator AROS. Here, we describe a molecular characterization of AROS and how it regulates Sirt1. We find that AROS is a partly intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) that inhibits rather than activates Sirt1. A biochemical characterization of the interaction including binding and stability assays, NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and a crystal structure of Sirtuin/AROS peptide complex reveal that AROS acts as a competitive inhibitor, through binding to the Sirt1 substrate peptide site. Our results provide molecular insights in the physiological regulation of Sirt1 by a regulator protein and suggest the peptide site as an opportunity for Sirt1-targeted drug development.
Keywords: Sirt1; activator; deacetylase; inhibitor; regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rauh D., Fischer F., Gertz M., Lakshminarasimhan M., Bergbrede T., Aladini F., Kambach C., Becker C.F.W., Zerweck J., Schutkowski M., et al. An acetylome peptide microarray reveals specificities and deacetylation substrates for all human sirtuin isoforms. Nat. Commun. 2013;4:2327. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

