GDNF Increases Inhibitory Synaptic Drive on Principal Neurons in the Hippocampus via Activation of the Ret Pathway
- PMID: 36361981
- PMCID: PMC9653719
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113190
GDNF Increases Inhibitory Synaptic Drive on Principal Neurons in the Hippocampus via Activation of the Ret Pathway
Abstract
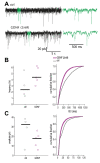
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) has been shown to counteract seizures when overexpressed or delivered into the brain in various animal models of epileptogenesis or chronic epilepsy. The mechanisms underlying this effect have not been investigated. We here demonstrate for the first time that GDNF enhances GABAergic inhibitory drive onto mouse pyramidal neurons by modulating postsynaptic GABAA receptors, particularly in perisomatic inhibitory synapses, by GFRα1 mediated activation of the Ret receptor pathway. Other GDNF receptors, such as NCAM or Syndecan3, are not contributing to this effect. We observed similar alterations by GDNF in human hippocampal slices resected from epilepsy patients. These data indicate that GDNF may exert its seizure-suppressant action by enhancing GABAergic inhibitory transmission in the hippocampal network, thus counteracting the increased excitability of the epileptic brain. This new knowledge can contribute to the development of novel, more precise treatment strategies based on a GDNF gene therapy approach.
Keywords: GDNF; IPSC; electrophysiology; epilepsy; ret.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









References
-
- Bespalov M.M., Sidorova Y.A., Tumova S., Ahonen-Bishopp A., Magalhães A.C., Kulesskiy E., Paveliev M., Rivera C., Rauvala H., Saarma M. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan Syndecan-3 Is a Novel Receptor for GDNF, Neurturin, and Artemin. J. Cell Biol. 2011;192:153–169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201009136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

