COVID-19 Molecular Pathophysiology: Acetylation of Repurposing Drugs
- PMID: 36362045
- PMCID: PMC9656873
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113260
COVID-19 Molecular Pathophysiology: Acetylation of Repurposing Drugs
Abstract
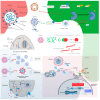
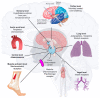
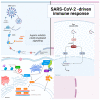
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) induces immune-mediated type 1 interferon (IFN-1) production, the pathophysiology of which involves sterile alpha motif and histidine-aspartate domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1) tetramerization and the cytosolic DNA sensor cyclic-GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling pathway. As a result, type I interferonopathies are exacerbated. Aspirin inhibits cGAS-mediated signaling through cGAS acetylation. Acetylation contributes to cGAS activity control and activates IFN-1 production and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling via STING. Aspirin and dapsone inhibit the activation of both IFN-1 and NF-κB by targeting cGAS. We define these as anticatalytic mechanisms. It is necessary to alleviate the pathologic course and take the lag time of the odds of achieving viral clearance by day 7 to coordinate innate or adaptive immune cell reactions.
Keywords: ACE2 (angiotensin-converting enzyme 2); SAMHD1 (sterile alpha motif and histidine-aspartate domain-containing protein 1); SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2); TLR4 (Toll-like receptor 4); aspirin; cGAS–STING (cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP)-adenosine monophosphate (AMP) synthase (cGAS)–stimulator of interferon genes (STING)); dapsone; dexamethasone; immunologic engram; inflammasome; spike protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Rodrigues T.S., de Sá K.S.G., Ishimoto A.Y., Becerra A., Oliveira S., Almeida L., Gonçalves A.V., Perucello D.B., Andrade W.A., Castro R., et al. Inflammasomes are activated in response to SARS-CoV-2 infection and are associated with COVID-19 severity in patients. J. Exp. Med. 2020;218:e20201707. doi: 10.1084/jem.20201707. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saris A., Reijnders T.D.Y., Nossent E.J., Schuurman A.R., Verhoeff J., van Asten S., Bontkes H., Blok S., Duitman J., Bogaard H.-J., et al. Distinct cellular immune profiles in the airways and blood of critically ill patients with COVID-19. Thorax. 2021;76:1010–1019. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216256. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wauters E., Van Mol P., Garg A.D., Jansen S., Van Herck Y., Vanderbeke L., Bassez A., Boeckx B., Malengier-Devlies B., Timmerman A., et al. Discriminating Mild from Critical COVID-19 by Innate and Adaptive Immune Single-cell Profiling of Bronchoalveolar Lavages. BioRxiv. 2021;31:272–290. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00455-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

