In Vitro and In Silico Analysis of New n-Butyl and Isobutyl Quinoxaline-7-carboxylate 1,4-di- N-oxide Derivatives against Trypanosoma cruzi as Trypanothione Reductase Inhibitors
- PMID: 36362102
- PMCID: PMC9655728
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113315
In Vitro and In Silico Analysis of New n-Butyl and Isobutyl Quinoxaline-7-carboxylate 1,4-di- N-oxide Derivatives against Trypanosoma cruzi as Trypanothione Reductase Inhibitors
Abstract
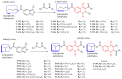
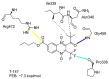
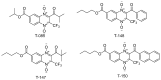
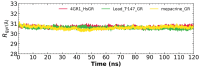
American trypanosomiasis is a worldwide health problem that requires attention due to ineffective treatment options. We evaluated n-butyl and isobutyl quinoxaline-7-carboxylate 1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives against trypomastigotes of the Trypanosoma cruzi strains NINOA and INC-5. An in silico analysis of the interactions of 1,4-di-N-oxide on the active site of trypanothione reductase (TR) and an enzyme inhibition study was carried out. The n-butyl series compound identified as T-150 had the best trypanocidal activity against T. cruzi trypomastigotes, with a 13% TR inhibition at 44 μM. The derivative T-147 behaved as a mixed inhibitor with Ki and Ki' inhibition constants of 11.4 and 60.8 µM, respectively. This finding is comparable to the TR inhibitor mepacrine (Ki = 19 µM).
Keywords: Chagas disease; chemical synthesis; quinoxaline-1,4-di-N-oxide; trypanothione reductase; trypomastigotes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Trypanocidal Activity of Quinoxaline 1,4 Di-N-oxide Derivatives as Trypanothione Reductase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2017 Feb 1;22(2):220. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020220. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28157150 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the effect of methyl 2-acetamide-3-methylquinoxaline-7-carboxylate 1,4-di-N-oxide on the relative expression of the trypanothione reductase gene in Trypanosoma cruzi epimastigotes.Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019 May;32(3 Special):1447-1452. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2019. PMID: 31551230
-
Trypanothione Reductase: A Target for the Development of Anti- Trypanosoma cruzi Drugs.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(11):939-946. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170315145410. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28302040 Review.
-
Rational design of nitrofuran derivatives: Synthesis and valuation as inhibitors of Trypanosoma cruzi trypanothione reductase.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Jan 5;125:1088-1097. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.10.055. Epub 2016 Oct 24. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27810595
-
Trypanothione Reductase and Superoxide Dismutase as Current Drug Targets for Trypanosoma cruzi: An Overview of Compounds with Activity against Chagas Disease.Curr Med Chem. 2017 May 31;24(11):1066-1138. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161227094049. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28025938 Review.
Cited by
-
Expanding the antiprotozoal activity and the mechanism of action of n-butyl and iso-butyl ester of quinoxaline-1,4-di-N-oxide derivatives against Giardia lamblia, Trichomonas vaginalis, and Entamoeba histolytica. An in vitro and in silico approach.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024 Dec;39(1):2413018. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2024.2413018. Epub 2024 Oct 29. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39470324 Free PMC article.
-
Repurposing of rabeprazole as an anti-Trypanosoma cruzi drug that targets cellular triosephosphate isomerase.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2231169. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2231169. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37401012 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Trypanothione Synthetase and Trypanothione Reductase: Development of Common Inhibitors to Tackle Trypanosomatid Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Aug 11;18(8):1182. doi: 10.3390/ph18081182. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Trypanothione Metabolism in Trypanosomatids.Molecules. 2024 May 9;29(10):2214. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102214. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Benznidazole to New Drugs: Nanotechnology Contribution in Chagas Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 7;24(18):13778. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813778. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762080 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO/Chagas Disease (American Trypanosomiasis) [(accessed on 18 March 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs340/en/
-
- Rajão M.A., Furtado C., Alves C.L., Passos-Silva D.G., de Moura M.B., Schamber-Reis B.L., Kunrath-Lima M., Zuma A.A., Vieira-da-Rocha J.P., Garcia J.B.F., et al. Unveiling Benznidazole’s mechanism of action through overexpression of DNA repair proteins in Trypanosoma cruzi. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2014;55:309–321. doi: 10.1002/em.21839. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vazquez-Jimenez L.K., Hernandez-Posada M.I., Paz-Gonzalez A.D., Nogueda-Torres B., Martinez-Vazquez A.V., Herrera-Mayorga V., Bocanegra-García V., Rivera G. Analysis of the Effect of Methyl 2-Acetamide-3-Methylquinoxaline-7-Carboxylate 1,4-Di-N-Oxide on the Relative Expression of the Trypanothione Reductase Gene in Trypanosoma Cruzi Epimastigotes. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019;32:1447–1452. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

