Inflammatory Mechanism of Brucella Infection in Placental Trophoblast Cells
- PMID: 36362199
- PMCID: PMC9657658
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113417
Inflammatory Mechanism of Brucella Infection in Placental Trophoblast Cells
Abstract
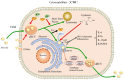
Brucellosis is a severe zoonotic infectious disease caused by the infection of the Brucella, which is widespread and causes considerable economic losses in underdeveloped areas. Brucella is a facultative intracellular bacteria whose main target cells for infection are macrophages, placental trophoblast cells and dendritic cells. The main clinical signs of Brucella infection in livestock are reproductive disorders and abortion. At present, the pathogenesis of placentitis or abortion caused by Brucella in livestock is not fully understood, and further research on the effect of Brucella on placental development is still necessary. This review will mainly introduce the research progress of Brucella infection of placental trophoblast cells as well as the inflammatory response caused by it, explaining the molecular regulation mechanism of Brucella leading to reproductive system disorders and abortion, and also to provide the scientific basis for revealing the pathogenesis and infection mechanism of Brucella.
Keywords: Brucella; infection mechanism; inflammatory response; pathogenesis; trophoblast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Shi B., Li X., Li B., Zheng N.X., Li M., Liu Y., Li C.H., Yan F., He W., Zhao L.Y., et al. Construction and evaluation of the Brucella double gene knock-out vaccine strain MB6 Δbp26ΔwboA (RM6) Zoonoses. 2022;2:29. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2022-0031. - DOI
-
- Erkyihun G.A., Gari F.R., Kassa G.M. Bovine brucellosis and its public health significance in Ethiopia. Zoonoses. 2022;2:15. doi: 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2022-0005. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

