Quantitative Analysis of Acetone in Transformer Oil Based on ZnO NPs@Ag NWs SERS Substrates Combined with a Stoichiometric Model
- PMID: 36362419
- PMCID: PMC9658008
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms232113633
Quantitative Analysis of Acetone in Transformer Oil Based on ZnO NPs@Ag NWs SERS Substrates Combined with a Stoichiometric Model
Abstract
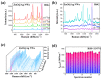
Acetone is an essential indicator for determining the aging of transformer insulation. Rapid, sensitive, and accurate quantification of acetone in transformer oil is highly significant in assessing the aging of oil-paper insulation systems. In this study, silver nanowires modified with small zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs@Ag NWs) were excellent surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates and efficiently and sensitively detected acetone in transformer oil. Stoichiometric models such as multiple linear regression (MLR) models and partial least square regressions (PLS) were investigated to quantify acetone in transformer oil and compared with commonly used univariate linear regressions (ULR). PLS combined with a preprocessing algorithm provided the best prediction model, with a correlation coefficient of 0.998251 for the calibration set, 0.997678 for the predictive set, a root mean square error in the calibration set (RMSECV = 0.12596 mg/g), and a prediction set (RMSEP = 0.11408 mg/g). For an acetone solution of 0.003 mg/g, the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) was the lowest among the three quantitative models. For a concentration of 7.29 mg/g, the MAPE was 1.60%. This method achieved limits of quantification and detections of 0.003 mg/g and 1 μg/g, respectively. In general, these results suggested that ZnO NPs@Ag NWs as SERS substrates coupled with PLS simply and accurately quantified trace acetone concentrations in transformer oil.
Keywords: SERS; ZnO NPs@Ag NWs; acetone; quantification; transformer oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Djamali M., Tenbohlen S. A Validated Online Algorithm for Detection of Fan Failures in Oil-Immersed Power Transformers. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2017;116:224–233. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.02.012. - DOI
-
- Okabe S., Kaneko S., Kohtoh M., Amimoto T. Analysis Results for Insulating Oil Components in Field Transformers. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2010;17:302–311. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2010.5412031. - DOI
-
- Aj C., Salam M.A., Rahman Q.M., Wen F., Ang S.P., Voon W. Causes of Transformer Failures and Diagnostic Methods—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018;82:1442–1456. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.165. - DOI
-
- Murugan R., Ramasamy R. Failure Analysis of Power Transformer for Effective Maintenance Planning in Electric Utilities. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2015;55:182–192. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.06.002. - DOI
-
- Metwally I.A. Failures, Monitoring and New Trends of Power Transformers. IEEE Potentials. 2011;30:36–43. doi: 10.1109/MPOT.2011.940233. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

