Use of Levosimendan in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure: An Update
- PMID: 36362634
- PMCID: PMC9659135
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11216408
Use of Levosimendan in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure: An Update
Abstract
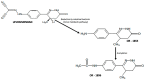
Levosimendan is an inodilator drug that, given its unique pharmacological actions and safety profile, represents a viable therapeutic option in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction in the advanced stage of the disease (advHFrEF). Pulsed levosimendan infusion in patients with advHFrEF improves symptoms and clinical and hemodynamic status, prevents recurrent hospitalizations, and enables optimization of guidelines-directed medical therapy. Furthermore, considering its proprieties on right ventricular function and pulmonary circulation, levosimendan could be helpful for the prevention and treatment of the right ventricular dysfunction post-implanting a left ventricular assist device. However, to date, evidence on this issue is scarce and has yielded mixed results. Finally, preliminary experiences indicate that treatment with levosimendan at scheduled intervals may serve as a "bridge to transplant" strategy in patients with advHFrEF. In this review, we summarized the clinical pharmacology of levosimendan, the available evidence in the treatment of patients with advHFrEF, as well as a hypothesis for its use in patients with advanced heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Keywords: advanced heart failure; inodilators; levosimendan; pharmacologic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
P.P. is a full-time employee of Orion Pharma, where levosimendan was discovered and developed. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fang J.C., Ewald G.A., Allen L.A., Butler J., Canary C.A.W., Colvin-Adams M., Dickinson M.G., Levy P., Stough W.G., Sweitzer N.K., et al. Advanced (Stage D) Heart Failure: A Statement from the Heart Failure Society of America Guidelines Committee. J. Card. Fail. 2015;21:519–534. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2015.04.013. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

