Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Solid Organ Transplant and Rejection Episodes in Brazil's Unified Healthcare System
- PMID: 36362809
- PMCID: PMC9658443
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11216581
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Solid Organ Transplant and Rejection Episodes in Brazil's Unified Healthcare System
Abstract
Background: Brazil has the world's largest public organ transplant program, which was severely affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. The primary aim of the study was to evaluate differences in solid organ transplants and rejection episodes during the COVID-19 pandemic compared to the five years before the pandemic in the country.
Methods: A seven-year database was built by downloading data from the DATASUS server. The pandemic period was defined as March 2020 to December 2021. The pre-pandemic period was from January 2015 to March 2020.
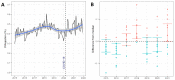
Results: During the pandemic, the number of solid organ transplants decreased by 19.3% in 2020 and 22.6% in 2021 compared to 2019. We found a decrease for each evaluated organ, which was more pronounced for lung, pancreas, and kidney transplants. The seasonal plot of rejection data indicated a high rejection rate between 2018 and 2021. There was also an 18% (IRR 1.18 (95% CI 1.01 to 1.37), p = 0.04) increase in the rejection rate during the COVID-19 pandemic.
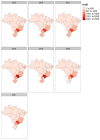
Conclusions: The total number of organ transplants performed in 2021 represents a setback of six years. Transplant procedures were concentrated in the Southeast region of the country, and a higher proportion of rejections occurred during the pandemic. Together, these findings could have an impact on transplant procedures and outcomes in Brazil.
Keywords: Brazil; COVID-19; graft rejection; organ transplant.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- DATASUS—Ministério Da Saúde. [(accessed on 21 July 2022)]; Available online: https://datasus.saude.gov.br/
-
- Requião-Moura L.R., Sandes-Freitas T.V., Viana L.A., Cristelli M.P., Andrade L.G.M., Garcia V.D., Oliveira C.M.C., Esmeraldo R.M., Abbud Filho M., Pacheco-Silva A., et al. High Mortality among Kidney Transplant Recipients Diagnosed with Coronavirus Disease 2019: Results from the Brazilian Multicenter Cohort Study. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0254822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254822. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

