Research on High-Temperature Evaluation Indexes and Performance of Qingchuan Rock-SBS Composite Modified Asphalt
- PMID: 36363047
- PMCID: PMC9654064
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15217455
Research on High-Temperature Evaluation Indexes and Performance of Qingchuan Rock-SBS Composite Modified Asphalt
Abstract
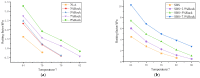
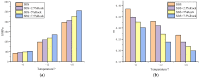
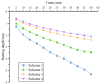
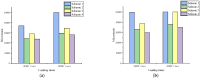
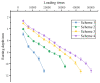
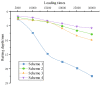
The phenomenon of structural destabilization damage to asphalt pavement is becoming increasingly serious as a result of high temperatures and heavy traffic. Considering the advantages of Qingchuan rock asphalt (QRA) in its durability, high-temperature rutting resistance, and good compatibility with asphalt, it was proposed to compound rock asphalt with SBS to ameliorate the high-temperature performance of asphalt. In this study, DSR and BBR were used to determine the rheological properties of Qingchuan rock-modified asphalt (QRMA) and Qingchuan rock-SBS-modified asphalt (QRA-SBSMA), and the optimum blending amount of rock asphalt was determined based on the PG classification results. Secondly, four different structures of '30 mm AC-10 upper layer (70-A, QRMA, SBSMA, QRA-SBSMA) + 50 mm AC-16 lower layer (70-A)' double-layer composite specimens were prepared. Multiple high-temperature performance evaluation indexes (G*/sinδ, Ds, rutting depth, micro-strain, Fn, modulus) were used to assess the improvement effect of QRA. Finally, using a 1/3 scale accelerated loading testing machine, we simulated high-temperature, water, and high-temperature coupled environments to assess the impact of high temperature and water on the performance of QRMA and QRA-SBSMA, respectively. The findings demonstrated that QRA can increase the PG classification of 70-A and SBSMA as well as its resistance to high-temperature deformation. Multi-index comprehensive evaluation methods were used to consummate the asphalt high-temperature evaluation system. The QRA-SBSMA had the smallest rutting depth and creep rate and the largest dynamic modulus, characterizing its ability to optimally resist high-temperature rutting and deformation.
Keywords: Qingchuan rock asphalt; double-layer composite structure; high-temperature evaluation; multiple evaluation indexes; road engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Wang W.T., Zhao K., Li J.F. Characterization of dynamic response of asphalt pavement in dry and saturated conditions using the full-scale accelerated loading test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;312:125355. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125355. - DOI
-
- Meroni F., Flintsch G.W., Habbouche J. Three-level performance evaluation of high RAP asphalt surface mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021;309:125164. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125164. - DOI
-
- Mana M., Gholamali S., Mohammad A. Evaluation of fatigue and rutting properties of asphalt binder and mastic modified by synthesized polyurethane. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021;8:1036–1048.
-
- Yan K.Z., Liu W.Y., You L.Y. Evaluation of waste cooling oil and European Rock Asphalt modified asphalt with laboratory tests and economic cost comparison. J. Clean. Prod. 2021;310:127364. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127364. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

