New Therapeutic Options in Mild Moderate COVID-19 Outpatients
- PMID: 36363723
- PMCID: PMC9697915
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10112131
New Therapeutic Options in Mild Moderate COVID-19 Outpatients
Abstract
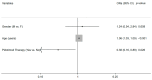
Background: In recent years, the therapeutic options for COVID have significantly improved; however, the therapies are expensive with restricted access to drugs, and expeditious and difficult to manage at home. We investigated the effect of pidotimod in preventing hospitalization in patients with mild-moderate COVID-19. Methods: A total of 1231 patients between January and June 2021 were screened. A total of 184 patients with mild-moderate COVID-19 were enrolled and divided into two groups: group-A (97) had undergone therapy with pidotimod 800 mg bid for 7−10 days and group-B (87) had other therapies. We excluded those who had undergone complete vaccination course, monoclonal anti-spike/antivirals or the co-administration of pidotimod-steroid. The primary outcome chosen was the emergency room, hospitalization, and deaths for COVID-related causes; the secondary outcome chosen was the duration of COVID-19 illness. Results: A total of 34 patients (18.5%) required hospital treatment, 11 in group-A and 23 in group-B (11.3% vs. 26.4%, p = 0.008). The median disease duration in group-A was 21 days (IQR 17−27) vs. 23 (IQR 20−31) in group-B (p = 0.005). Patients in the pidotimod group had higher SpO2 in the walking test (IQR 96−99% vs. IQR 93−98%, p = 0.01) and a lower need for steroid rescue therapy (11.5% vs. 60.9%, p < 0.001). Conclusions: In the first phase of disease, pidotimod can represent an effective, low-cost, weapon, without restrictions of use, that is able to prevent a second aggressive phase and promote faster virological recovery.
Keywords: SARS-CoV2; efficacy; immunomodulation; pidotimod; safety; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- [(accessed on 29 September 2022)]. Available online: www.coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Yang X., Yu Y., Xu J., Shu H., Xia J., Liu H., Wu Y., Zhang L., Yu Z., Fang M., et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020;8:475–481. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous