Uncovering the Anticancer Potential of Polydatin: A Mechanistic Insight
- PMID: 36364001
- PMCID: PMC9656535
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217175
Uncovering the Anticancer Potential of Polydatin: A Mechanistic Insight
Abstract
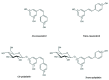
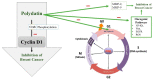
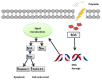
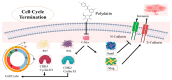
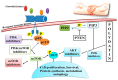
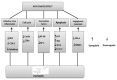
Polydatin or 3-O-β-d-resveratrol-glucopyranoside (PD), a stilbenoid component of Polygonum cuspicadum (Polygonaceae), has a variety of biological roles. In traditional Chinese medicine, P. cuspicadum extracts are used for the treatment of infections, inflammation, and cardiovascular disorders. Polydatin possesses a broad range of biological activities including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and hepatoprotective, neuroprotective, and immunostimulatory effects. Currently, a major proportion of the population is victimized with cervical lung cancer, ovarian cancer and breast cancer. PD has been recognized as a potent anticancer agent. PD could effectively inhibit the migration and proliferation of ovarian cancer cells, as well as the expression of the PI3K protein. The malignancy of lung cancer cells was reduced after PD treatments via targeting caspase 3, arresting cancer cells at the S phase and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome by downregulation of the NF-κB pathway. This ceases cell cycle, inhibits VEGF, and counteracts ROS in breast cancer. It also prevents cervical cancer by regulating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), apoptosis, and the C-Myc gene. The objective of this review is thus to unveil the polydatin anticancer potential for the treatment of various tumors, as well as to examine the mechanisms of action of this compound.
Keywords: 3-O-β-d-resveratrol-glucopyranoside; breast cancer; cervical cancer; lung cancer; ovarian cancer; phenol compounds; polydatin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- National Cancer Institute What Is Cancer. [(accessed on 5 May 2021)]; Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer.
-
- WHO Cancer Prevalence. [(accessed on 26 March 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer#:~:text=I....
-
- WHO, Cervical Cancer Prevalence. [(accessed on 22 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer.
-
- Medscape, Non Small Lung Cancer. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)]. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/279960-overview.
-
- SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD, USA. [(accessed on 3 August 2022)]; Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

