Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Different Vegetable Sprouts and Their Potential Role in the Formulation of Functional Foods against Various Disorders: A Literature-Based Review
- PMID: 36364145
- PMCID: PMC9658993
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217320
Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Different Vegetable Sprouts and Their Potential Role in the Formulation of Functional Foods against Various Disorders: A Literature-Based Review
Abstract
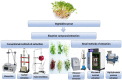
In this review, we discuss the advantages of vegetable sprouts in the development of food products as well as their beneficial effects on a variety of disorders. Sprouts are obtained from different types of plants and seeds and various types of leafy, root, and shoot vegetables. Vegetable sprouts are enriched in bioactive compounds, including polyphenols, antioxidants, and vitamins. Currently, different conventional methods and advanced technologies are used to extract bioactive compounds from vegetable sprouts. Due to some issues in traditional methods, increasingly, the trend is to use recent technologies because the results are better. Applications of phytonutrients extracted from sprouts are finding increased utility for food processing and shelf-life enhancement. Vegetable sprouts are being used in the preparation of different functional food products such as juices, bread, and biscuits. Previous research has shown that vegetable sprouts can help to fight a variety of chronic diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Furthermore, in the future, more research is needed that explores the extraordinary ways in which vegetable sprouts can be incorporated into green-food processing and preservation for the purpose of enhancing shelf-life and the formation of functional meat products and substitutes.
Keywords: bioactive compound; functional product; new extraction; pharmacological role; sprout.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Total polyphenols and bioactivity of seeds and sprouts in several legumes.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(34):6112-24. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319340005. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23448441 Review.
-
Polyphenol composition and antioxidant properties of vegetable leaf-fortified bread.J Food Biochem. 2019 Jun;43(6):e12625. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12625. Epub 2018 Aug 3. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31353621
-
Incorporating dietary fiber from fruit and vegetable waste in meat products: a systematic approach for sustainable meat processing and improving the functional, nutritional and health attributes.PeerJ. 2023 Mar 1;11:e14977. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14977. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36890873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isolation of bioactive peptides and multiple nutraceuticals of antidiabetic and antioxidant functionalities through sprouting: Recent advances.J Food Biochem. 2022 Oct;46(10):e14317. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14317. Epub 2022 Jul 22. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35867040 Review.
-
Amaranth Seeds and Sprouts as Functional Ingredients for the Development of Dietary Fiber, Betalains, and Polyphenol-Enriched Minced Tilapia Meat Gels.Molecules. 2022 Dec 23;28(1):117. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010117. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615309 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Influence of Polyphenols on Atherosclerosis Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 12;24(8):7146. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087146. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Infectivity responses of Salmonella enterica to bacteriophages on maize seeds and maize sprouts.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Feb 25;8:100708. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100708. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 38444730 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative Approaches to Soybean Resilience, Productivity, and Utility: A Review of Genomics, Computational Modeling, and Economic Viability.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 21;14(5):671. doi: 10.3390/plants14050671. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40094561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of Germinated Seeds as Functional Food Ingredients: Optimization of Nutrient Composition and Antioxidant Activity Evolution Based on the Germination Characteristics of Chinese Chestnut (Castanea mollissima).Foods. 2024 Aug 20;13(16):2605. doi: 10.3390/foods13162605. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200532 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Eating Habits, Healthy Food Awareness, and Inclination toward Functional Foods of Italian Elderly People through Computer-Assisted Telephone Interviews (CATIs).Nutrients. 2024 Mar 7;16(6):762. doi: 10.3390/nu16060762. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38542674 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu H.K., Kang Y.F., Zhao X.Y., Liu Y.P., Zhang X.W., Zhang S.J. Effects of elicitation on bioactive compounds and biological activities of sprouts. J. Funct. Foods. 2019;53:136–145. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.12.019. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources