Preparation and Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Flavonoids: Review and Perspective
- PMID: 36364181
- PMCID: PMC9653670
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217355
Preparation and Application of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Flavonoids: Review and Perspective
Abstract
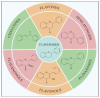
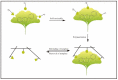
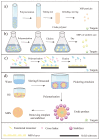
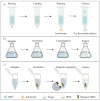
The separation and detection of flavonoids from various natural products have attracted increasing attention in the field of natural product research and development. Depending on the high specificity of molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs), MIPs are proposed as efficient adsorbents for the selective extraction and separation of flavonoids from complex samples. At present, a comprehensive review article to summarize the separation and purification of flavonoids using molecular imprinting, and the employment of MIP-based sensors for the detection of flavonoids is still lacking. Here, we reviewed the general preparation methods of MIPs towards flavonoids, including bulk polymerization, precipitation polymerization, surface imprinting and emulsion polymerization. Additionally, a variety of applications of MIPs towards flavonoids are summarized, such as the different forms of MIP-based solid phase extraction (SPE) for the separation of flavonoids, and the MIP-based sensors for the detection of flavonoids. Finally, we discussed the advantages and disadvantages of the current synthetic methods for preparing MIPs of flavonoids and prospected the approaches for detecting flavonoids in the future. The purpose of this review is to provide helpful suggestions for the novel preparation methods of MIPs for the extraction of flavonoids and emerging applications of MIPs for the detection of flavonoids from natural products and biological samples.
Keywords: applications; flavonoids; molecularly imprinted polymers; natural products; preparation methods.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Middleton E., Jr., Kandaswami C., Theoharides T.C. The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells: Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2000;52:673–751. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

