Sensitive and Facile HCOOH Fluorescence Sensor Based on Highly Active Ir Complexes' Catalytic Transfer Hydrogen Reaction
- PMID: 36364257
- PMCID: PMC9656036
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217431
Sensitive and Facile HCOOH Fluorescence Sensor Based on Highly Active Ir Complexes' Catalytic Transfer Hydrogen Reaction
Abstract
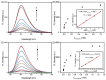
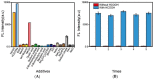
With several major polarity and weak optical properties, the sensitive detection of HCOOH remains a major challenge. Given the special role of HCOOH in assisting in the catalytic hydrogenation process of Ir complexes, HCOOH (as a hydrogen source) could rapidly activate Ir complexes as catalysts and further reduce the substrates. This work developed a facile and sensitive HCOOH fluorescence sensor utilizing an optimal catalytic fluorescence generation system, which consists of the phenyl-pyrazole-type Ir-complex PP-Ir-Cl and the coumarin-type fluorescence probe P-coumarin. The sensor demonstrates excellent sensitivity and specificity for HCOOH and formates; the limits of detection for HCOOH, HCOONa, and HCOOEt3N were tested to be 50.6 ppb, 68.0 ppb, and 146.0 ppb, respectively. Compared to previous methods, the proposed sensor exhibits good detection accuracy and excellent sensitivity. Therefore, the proposed HCOOH sensor could be used as a new detection method for HCOOH and could provide a new design path for other sensors.
Keywords: HCOOH detection; Ir complexes; catalytic hydrogenation; fluorescence probe.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Li L., Zhao N., Wei W., Sun Y. A review of research progress on CO2 capture, storage, and utilization in Chinese Academy of Sciences. Fuel. 2013;108:112–130. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2011.08.022. - DOI
-
- Rahman F.A., Aziz M.M.A., Saidur R., Bakar W.A.W.A., Hainin M.R., Putrajaya R., Hassan N.A. Pollution to solution: Capture and sequestration of carbon dioxide (CO2) and its utilization as a renewable energy source for a sustainable future. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017;71:112–126. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.011. - DOI
-
- Sun M., Zhao B., Chen F., Liu C., Lu S., Yu Y., Zhang B. Thermally-assisted photocatalytic CO2 reduction to fuels. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;408:127280. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127280. - DOI
-
- Ganesh I. Conversion of carbon dioxide into methanol—A potential liquid fuel: Fundamental challenges and opportunities (a review) Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014;31:221–257. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.11.045. - DOI
-
- Chen L., Guo Z., Wei X.G., Gallenkamp C., Bonin J., Anxolabehere-Mallart E., Lau K.C., Lau T.C., Robert M. Molecular Catalysis of the Electrochemical and Photochemical Reduction of CO2 with Earth-Abundant Metal Complexes. Selective Production of CO vs. HCOOH by Switching of the Metal Center. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015;137:10918–10921. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b06535. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

