Identification of Boronate-Containing Diarylpyrimidine Derivatives as Novel HIV-1 Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
- PMID: 36364360
- PMCID: PMC9657321
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217538
Identification of Boronate-Containing Diarylpyrimidine Derivatives as Novel HIV-1 Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors
Abstract
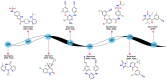
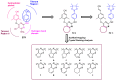
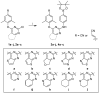
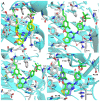
In this study, privileged boronic acid ester was introduced into the right wing of etravirine (ETR) to obtain a series of novel boronate-containing derivatives. These newly synthesized derivatives were evaluated for their anti-HIV potency in MT-4 cells using the MTT method, and their inhibitory activity to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) was assayed by the ELISA method. Most of the synthesized compounds displayed promising antiviral activity against the wild-type and a wide range of HIV-1 mutant strains. In particular, 4a exhibited the most potent activity against the wild-type and a panel of single mutations (L100I, K103N, Y181C, and E138K) with EC50 values ranging from 0.005 to 0.648 μM, which were much superior to those of nevirapine (EC50 = 0.151 μM). Moreover, 4b turned out to be an effective inhibitor against the double-mutant strains F227L + V106A and RES056 with EC50 values of 3.21 and 2.30 μM, respectively. RT inhibition activity and molecular docking were also investigated.
Keywords: DAPY; HIV-1; NNIBP; NNRTIs; boronate; drug design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Feng D., Zuo X., Jing L., Chen C.H., Olotu F.A., Lin H., Soliman M., De Clercq E., Pannecouque C., Lee K.H., et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of “dual-site”-binding diarylpyrimidines targeting both NNIBP and the NNRTI adjacent site of the HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021;211:113063. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.113063. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

