Indole-Containing Natural Products 2019-2022: Isolations, Reappraisals, Syntheses, and Biological Activities
- PMID: 36364413
- PMCID: PMC9655573
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217586
Indole-Containing Natural Products 2019-2022: Isolations, Reappraisals, Syntheses, and Biological Activities
Abstract
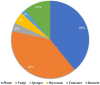
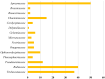
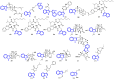
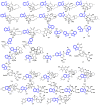
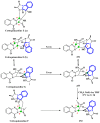
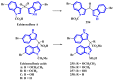
Indole alkaloids represent a large subset of natural products, with more than 4100 known compounds. The majority of these alkaloids are biologically active, with some exhibiting excellent antitumor, antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, and antiplasmodial activities. Consequently, the natural products of this class have attracted considerable attention as potential leads for novel therapeutics and are routinely isolated, characterized, and profiled to gauge their biological potential. However, data on indole alkaloids, their various structures, and bioactivities are complex due to their diverse sources, such as plants, fungi, bacteria, sponges, tunicates, and bryozoans; thus, isolation methods produce an incredible trove of information. The situation is exacerbated when synthetic derivatives, as well as their structures, bioactivities, and synthetic schemes, are considered. Thus, to make such data comprehensive and inform researchers about the current field's state, this review summarizes recent reports on novel indole alkaloids. It deals with the isolation and characterization of 250 novel indole alkaloids, a reappraisal of previously reported compounds, and total syntheses of indole alkaloids. In addition, several syntheses and semi-syntheses of indole-containing derivatives and their bioactivities are reported between January 2019 and July 2022.
Keywords: anticancer; antimicrobial; antiviral; cytotoxic; indole; natural products; other bioactivities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
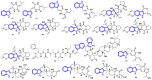
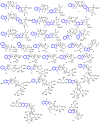

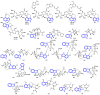
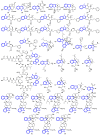
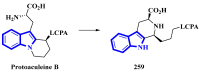
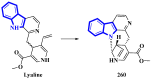
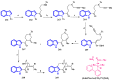
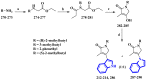
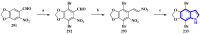
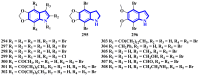
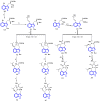
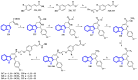

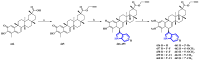
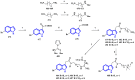
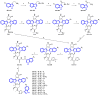
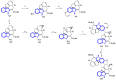

References
-
- Lahlou M. The success of natural products in drug discovery. Pharmacol. Pharm. 2013;4:17–31. doi: 10.4236/pp.2013.43A003. - DOI
-
- John J.E. Natural products-based drug discovery: Some bottlenecks and considerations. Curr. Sci. 2009;96:753–754.
-
- Appendino G., Fontana G., Pollastro F. Natural Products Drug Discovery. In: Liu H.-W., Mander L., editors. Comprehensive Natural Products II. Elsevier; Oxford, UK: 2010. pp. 205–236.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

