Fabrication of Novel Bentonite-Anthracite@Zetag (BT-An@Zetag) Composite for the Removal of Arsenic (V) from an Aqueous Solution
- PMID: 36364462
- PMCID: PMC9659286
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27217635
Fabrication of Novel Bentonite-Anthracite@Zetag (BT-An@Zetag) Composite for the Removal of Arsenic (V) from an Aqueous Solution
Abstract
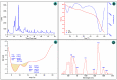
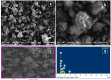
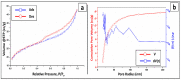
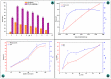
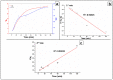
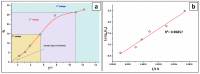
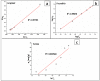
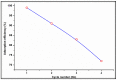
The arsenic (As) pollution of water has been eliminated via intensive scientific efforts, with the purpose of giving safe drinking water to millions of people across the world. In this study, the adsorption of As(V) from a synthetic aqueous solution was verified using a Bentonite-Anthracite@Zetag (BT-An@Zetag) composite. The SEM, FT-IR, XRD, DSC, TGA, and SBET techniques were used to characterize the (BT-An@Zetag) composite. The adsorption of As(V) was explored using batch adsorption under varied operating scenarios. Five kinetic modelswere used to investigate kinetic data, whereas three isotherms had been used to fit empirical equilibrium data. According to the findings, the adsorption mechanism of As(V) was best described by the Freundlich isotherm with a maximum monolayer coverage of 38.6 mg/g showing pseudo-second-order mode. The estimated enthalpy (H°) indicates that the adsorption process is both chemical and endothermic.The calculated free energy (G°) indicates that the reaction is nonspontaneous. After four sequential adsorption cycles, the produced BT-An@Zetag composite demonstrated good reusability and a greater adsorption affinity for As(V) ions. Overall, the BT-An@Zetag composite is suited for removing arsenic from wastewater using adsorption as a cost-effective and efficient technique.
Keywords: As(V); anthracite; arsenic; bentonite; composites; water pollutant; water treatment; zetag.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Arsenic Compounds (Environmental Health Criteria 224) World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2001.
-
- Stüben D., Berner Z., Chandrasekharam D., Karmakar J. Arsenic Enrichment in Groundwater of West Bengal, India: Geochemical Evidence for Mobilization of as under Reducing Conditions. Appl. Geochem. 2003;18:1417–1434. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(03)00060-X. - DOI
-
- Khan T., Chaudhuri M. Adsorption of Arsenate from Aqueous Solution by Rice Husk-Based Adsorbent; Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; Putrajaya, Malaysia. 5–6 March 2013; Bristol, UK: IOP Publishing; 2013. p. 12095.
-
- McGraw Hill Encyclopedia of Science & Technology (Mcgraw Hill Encyclopedia of Science And Technology) McGraw-Hill Yearbook of Science and Technology. McGraw-Hill Companies; New York, NY, USA: 1982.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

