Integrating Women and Girls' Nutrition Services into Health Systems in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36364750
- PMCID: PMC9657561
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14214488
Integrating Women and Girls' Nutrition Services into Health Systems in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Review
Abstract
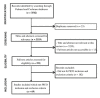
Women's nutrition has been highlighted as a global priority to ensure the health and well-being of both them and future generations. This systematic review summarises the available literature on the integration of nutrition services for girls and women of reproductive age (GWRA) into existing public health systems across low- and middle-income countries, as well as any barriers to integration. We searched PubMed and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews for articles published since 2011 according to eligibility criteria. A total of 69 articles were included. Evidence suggested that several services for GWRA are well integrated into public health systems, including antenatal care services, nutrition education and counselling, and micronutrient supplementation programmes. However, there was limited evidence on the integration of family planning, adolescent health, and reproductive health services. Barriers to integration fell into five main themes: lack of training and capacity building, poor multisectoral linkages and coordination, weak advocacy, lack of M&E systems, and inequity. We identified a lack of evidence and services for non-pregnant GWRA and for women postpartum. Addressing barriers to integration and gaps in nutrition services for GWRA would increase service coverage and contribute to improving health outcomes for GWRA and future generations.
Keywords: integration; interventions; public health systems; reproductive age; women’s nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fall C. Maternal nutrition: Effects on health in the next generation. [(accessed on 20 May 2021)];Indian J. Med. Res. 2009 130:593–599. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20090113/ - PubMed
-
- Fox E.L., Davis C., Downs S.M., Schultink W., Fanzo J. Who is the Woman in Women’s Nutrition? A Narrative Review of Evidence and Actions to Support Women’s Nutrition throughout Life. Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2018;3:nzy076. doi: 10.1093/cdn/nzy076. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources