Chiliadenus iphionoides Reduces Body Weight and Improves Parameters Related to Hepatic Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in a High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mice Model of NAFLD
- PMID: 36364811
- PMCID: PMC9657349
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14214552
Chiliadenus iphionoides Reduces Body Weight and Improves Parameters Related to Hepatic Lipid and Glucose Metabolism in a High-Fat-Diet-Induced Mice Model of NAFLD
Abstract
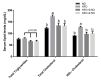
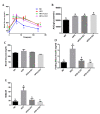
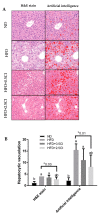
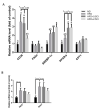
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become an epidemic with increasing prevalence. Limited treatment options and poor adherence emphasize the urgent need for novel therapies for the treatment and/or prevention of NAFLD. Bioactive natural compounds found in medicinal plants are promising as novel therapeutic agents for NAFLD. Chiliadenus iphionoides, a medicinal plant with several health-promoting properties, is an encouraging candidate. The current study aimed to elucidate the metabolic effects of C. iphionoides consumption in a high-fat-diet (HFD)-induced model of NAFLD. Male C57BL/6J mice (n = 40, 7-8-week-old) were fed a HFD (60% fat) with/without 0.5 or 2.5 gr C. iphionoides for fifteen weeks. Diet supplementation with C. iphionoides significantly ameliorated HFD-induced weight gain. Likewise, liver and adipose tissue weights were profoundly lower in the C. iphionoides-fed groups. Reduced liver steatosis in those groups was corroborated by histology, plasma liver enzyme levels, and lipid profile, indicating improved liver function and lipid metabolism in addition to enhanced insulin sensitivity. The addition of C. iphionoides to an obesogeneic diet can beneficially alleviate metabolic alterations and may be a practicable strategy for the management of NAFLD.
Keywords: Chiliadenus iphionoides; NAFLD; glucose tolerance; lipid metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective Effect of Seed Coat ofEuryale ferox Extract in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Induced by High-fat Diet in Mice by Increasing IRs-1 and Inhibiting CYP2E1.J Oleo Sci. 2019 Jun 6;68(6):581-589. doi: 10.5650/jos.ess19018. Epub 2019 May 16. J Oleo Sci. 2019. PMID: 31092797
-
1,2,3,4,6 penta-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose ameliorates high-fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and maintains the expression of genes involved in lipid homeostasis in mice.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Sep;129:110348. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110348. Epub 2020 Jun 15. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32554245
-
Can Zinc Supplementation Attenuate High Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 16;24(2):1763. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021763. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675277 Free PMC article.
-
The promising roles of medicinal plants and bioactive compounds on hepatic lipid metabolism in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in animal models: molecular targets.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023 Dec;129(6):1262-1278. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2021.1939387. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 34153200 Review.
-
Bioactive Compounds from Brown Algae Alleviate Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Extensive Review.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Feb 1;71(4):1771-1787. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c06578. Epub 2023 Jan 23. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 36689477 Review.
Cited by
-
Ophiopogonin D ameliorates non‑alcoholic fatty liver disease in high‑fat diet‑induced obese mice by improving lipid metabolism, oxidative stress and inflammatory response.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Jul 13;26(3):418. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.12116. eCollection 2023 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37602303 Free PMC article.
-
The Genus Chiliadenus: A Comprehensive Review of Taxonomic Aspects, Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 13;14(2):205. doi: 10.3390/plants14020205. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asteraceae Seeds as Alternative Ingredients in a Fibre-Rich Diet: Protein Quality and Metabolic Effects in Rats.Molecules. 2023 Apr 6;28(7):3275. doi: 10.3390/molecules28073275. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37050040 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Impacts of Aphanizomenon Flos Aquae Extract on Obesity-Related Dysmetabolism in Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity.Cells. 2023 Nov 25;12(23):2706. doi: 10.3390/cells12232706. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067134 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Interventions with Bletilla striata Polysaccharides and/or Composite Polysaccharides Remodel Liver Lipid Profiles and Ameliorate Gut Metabolic Disturbances in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Foods. 2025 Jul 29;14(15):2653. doi: 10.3390/foods14152653. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40807590 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

