A First Report of Molecular Typing, Virulence Traits, and Phenotypic and Genotypic Resistance Patterns of Newly Emerging XDR and MDR Aeromonas veronii in Mugil seheli
- PMID: 36365013
- PMCID: PMC9695981
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11111262
A First Report of Molecular Typing, Virulence Traits, and Phenotypic and Genotypic Resistance Patterns of Newly Emerging XDR and MDR Aeromonas veronii in Mugil seheli
Abstract
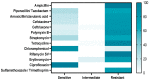
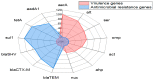
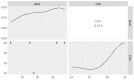
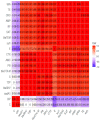
Aeromonas veronii is associated with substantial economic losses in the fish industry and with food-borne illness in humans. This study aimed to determine the prevalence, antibiogram profiles, sequence analysis, virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes, and pathogenicity of A. veronii recovered from Mugil seheli. A total of 80 fish were randomly gathered from various private farms in Suez Province, Egypt. Subsequently, samples were subjected to clinical, post-mortem, and bacteriological examinations. The retrieved isolates were tested for sequence analysis, antibiogram profile, pathogenicity, and PCR detection of virulence and resistance genes. The prevalence of A. veronii in the examined M. seheli was 22.5 % (18/80). The phylogenetic analyses revealed that the tested A. veronii strains shared high genetic similarity with other A. veronii strains from India, UK, and China. Using PCR it was revealed that the retrieved A. veronii isolates harbored the aerA, alt, ser, ompAII, act, ahp, and nuc virulence genes with prevalence of 100%, 82.9%, 61.7%, 55.3%, 44.7%, 36.17%, and 29.8%, respectively. Our findings revealed that 29.8% (14/47) of the retrieved A. veronii strains were XDR to nine antimicrobial classes and carried blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaSHV,tetA, aadA1, and sul1 resistance genes. Likewise, 19.1% (9/47) of the obtained A. veronii strains were MDR to eight classes and possessed blaTEM, blaCTX-M, blaSHV,tetA, aadA1, and sul1 genes. The pathogenicity testing indicated that the mortality rates positively correlated with the prevalence of virulence-determinant genes. To our knowledge, this is the first report to reveal the occurrence of XDR and MDR A. veronii in M. seheli, an emergence that represents a risk to public health. Emerging XDR and MDR A. veronii in M. seheli frequently harbored aerA, alt, ser, ompAII, and act virulence genes, and blaTEM, sul1, tetA, blaCTX-M, blaSHV, and aadA1 resistance genes.
Keywords: A. veronii; XDR; antimicrobial resistance genes; pathogenicity; sequence analysis; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Newly Emerging MDR B. cereus in Mugil seheli as the First Report Commonly Harbor nhe, hbl, cytK, and pc-plc Virulence Genes and bla1, bla2, tetA, and ermA Resistance Genes.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Apr 24;15:2167-2185. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S365254. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35498633 Free PMC article.
-
atpD gene sequencing, multidrug resistance traits, virulence-determinants, and antimicrobial resistance genes of emerging XDR and MDR-Proteus mirabilis.Sci Rep. 2021 May 4;11(1):9476. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88861-w. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33947875 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance profiles, virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes of XDR S. Enteritidis and S. Typhimurium.AMB Express. 2023 Oct 10;13(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s13568-023-01615-x. AMB Express. 2023. PMID: 37817026 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic, molecular detection, and Antibiotic Resistance Profile (MDR and XDR) of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from Farmed Tilapia zillii and Mugil cephalus.BMC Vet Res. 2024 Mar 8;20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03942-y. BMC Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38459543 Free PMC article.
-
oprL Gene Sequencing, Resistance Patterns, Virulence Genes, Quorum Sensing and Antibiotic Resistance Genes of XDR Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Broiler Chickens.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Feb 13;16:853-867. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S401473. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 36818807 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A unique combination of natural fatty acids from Hermetia illucens fly larvae fat effectively combats virulence factors and biofilms of MDR hypervirulent mucoviscus Klebsiella pneumoniae strains by increasing Lewis acid-base/van der Waals interactions in bacterial wall membranes.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 25;14:1408179. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1408179. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39119288 Free PMC article.
-
Colistin-, cefepime-, and levofloxacin-resistant Salmonella enterica serovars isolated from Egyptian chicken carcasses.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024 Jul 4;23(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12941-024-00713-3. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2024. PMID: 38965586 Free PMC article.
-
Extensively and multidrug-resistant bacterial strains: case studies of antibiotics resistance.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 4;15:1381511. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1381511. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39027098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High variation across E. coli hybrid isolates identified in metabolism-related biological pathways co-expressed with virulent genes.Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2228042. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2228042. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 37417543 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility profiles and resistant gene identification of bovine subclinical mastitis pathogens in Bangladesh.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 14;10(14):e34567. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34567. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39816335 Free PMC article.
References
-
- FAO . The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture. Contributing to Food Security and Nutrition for All. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2016.
-
- Abouelmaatti R.R., Algammal A.M., LI X., MA J., Abdelnaby E.A., Elfeil W.M. Cloning and analysis of Nile tilapia Toll-like receptors type-3 mRNA. Centr. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013;38:277–282. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2013.37740. - DOI
-
- Shaalan M., El-Mahdy M., Saleh M., El-Matbouli M. Aquaculture in Egypt: Insights on the Current Trends and Future Perspectives for Sustainable Development. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2018;26:99–110. doi: 10.1080/23308249.2017.1358696. - DOI
-
- Mehanna S.F., El-Sherbeny A.S., El-Mor M., Eid N.M. Age, Growth and Mortality of Liza Carinata Valenciennes, 1836 (Pisces: Mugilidae) in Bitter Lakes, Suez Canal, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019;23:283–290. doi: 10.21608/ejabf.2019.47938. - DOI
-
- Nelson J.S. Fishes of the World. 4th ed. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

