Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) Tolerance to Cadmium: A Case Study of Proteome and Metabolome of Four Different Flax Genotypes
- PMID: 36365383
- PMCID: PMC9655427
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11212931
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) Tolerance to Cadmium: A Case Study of Proteome and Metabolome of Four Different Flax Genotypes
Abstract
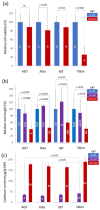
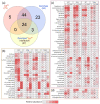
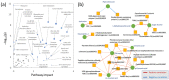
Cadmium is one of the most toxic heavy metal pollutants, and its accumulation in the soil is harmful to agriculture. Plants have a higher cadmium tolerance than animals, and some species can be used for phytoremediation. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) can accumulate high amounts of cadmium, but the molecular mechanism behind its tolerance is unknown. Here, we employed four genotypes representing two fiber cultivars, an oilseed breeding line, and a transgenic line overexpressing the metallothionein domain for improved cadmium tolerance. We analyzed the proteome of suspensions and the proteome and metabolome of seedling roots in response to cadmium. We identified more than 1400 differentially abundant proteins representing putative mechanisms in cadmium tolerance, including metal-binding proteins and transporters, enzymes of flavonoid, jasmonate, polyamine, glutathione metabolism, and HSP70 proteins. Our data indicated the role of the phytohormone cytokinin in the observed responses. The metabolome profiling found that pipecolinic acid could be a part of the cadmium accumulation mechanism, and the observed accumulation of putrescine, coumaric acid, cinnamic acid, and coutaric acid confirmed the role of polyamines and flavonoids in tolerance to cadmium. In conclusion, our data provide new insight into cadmium tolerance and prospective targets for improving cadmium tolerance in other plants.
Keywords: Cd2+; HSP70; heavy metals; phenolic compounds; pipecolinic acid; polyamines; proteome; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Hashem A., Abd_Allah E.F., Alqarawi A.A., Al Huqail A.A., Egamberdieva D., Wirth S. Alleviation of cadmium stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi via induction of acquired systemic tolerance. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016;23:272–281. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.11.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang M.-K., Liu Z.-Y., Wang H. Use of Single Extraction Methods to Predict Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Polluted Soils to Rice. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010;41:820–831. doi: 10.1080/00103621003592341. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

