Three-Stage Pavement Crack Localization and Segmentation Algorithm Based on Digital Image Processing and Deep Learning Techniques
- PMID: 36366156
- PMCID: PMC9656577
- DOI: 10.3390/s22218459
Three-Stage Pavement Crack Localization and Segmentation Algorithm Based on Digital Image Processing and Deep Learning Techniques
Abstract
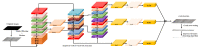
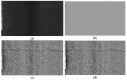
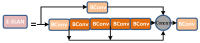
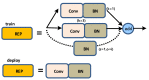
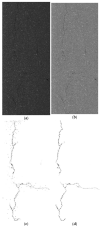
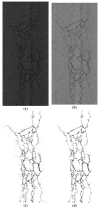
The image of expressway asphalt pavement crack disease obtained by a three-dimensional line scan laser is easily affected by external factors such as uneven illumination distribution, environmental noise, occlusion shadow, and foreign bodies on the pavement. To locate and extract cracks accurately and efficiently, this article proposes a three-stage asphalt pavement crack location and segmentation method based on traditional digital image processing technology and deep learning methods. In the first stage of this method, the guided filtering and Retinex methods are used to preprocess the asphalt pavement crack image. The processed image removes redundant noise information and improves the brightness. At the information entropy level, it is 63% higher than the unpreprocessed image. In the second stage, the newly proposed YOLO-SAMT target detection model is used to locate the crack diseases in asphalt pavement. The model is 5.42 percentage points higher than the original YOLOv7 model on mAP@0.5, which enhances the recognition and location ability of crack diseases and reduces the calculation amount for the extraction of crack contour in the next stage. In the third stage, the improved k-means clustering algorithm is used to extract cracks. Compared with the traditional k-means clustering algorithm, this method improves the accuracy by 7.34 percentage points, the true rate by 6.57 percentage points, and the false positive rate by 18.32 percentage points to better extract the crack contour. To sum up, the method proposed in this article improves the quality of the pavement disease image, enhances the ability to identify and locate cracks, reduces the amount of calculation, improves the accuracy of crack contour extraction, and provides a new solution for highway crack inspection.
Keywords: Retinex; YOLOv7; asphalt pavement crack; attention mechanism; deep learning; digital image processing technology; guided filter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
















References
-
- Cheng H.-D., Chen J.-R., Glazier C. Novel fuzzy logic approach to pavement distress detection. In: Chase S.B., editor. Nondestructive Evaluation of Bridges and Highways. SPIE; Bellingham, WA, USA: 1996.
-
- Zuo Y., Wang G., Zuo C. Wavelet Packet Denoising for Pavement Surface Cracks Detection; Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Security; Suzhou, China. 13–17 December 2008.
-
- Bhutani K.R., Battou A. An Application of Fuzzy Relations to Image Enhancement. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 1995;16:901–909. doi: 10.1016/0167-8655(95)00035-F. - DOI
-
- Kirschke K.R., Velinsky S.A. Histogram-based Approach for Automated Pavement-crack Sensing. J. Transp. Eng. 1992;118:700–710. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-947X(1992)118:5(700). - DOI
-
- Oliveira H., Correia L. Automatic Road Crack Segmentation Using Entropy and Image Dynamic Thresholding; Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference; Glasgow, UK. 24–28 August 2009; pp. 2252–2259.
Grants and funding
- 2021YFB3202901/The National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2020H6009/Major Project of Industry-University Cooperation Science and Technology in Universities in Fujian Province
- RCS2020K004/The State Key Laboratory of Rail Traffic Control and Safety,Beijing Jiaotong University
- Beijing Jiaotong University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

