Healthcare Worker Study Cohort to Determine the Level and Durability of Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination
- PMID: 36366293
- PMCID: PMC9697204
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10111784
Healthcare Worker Study Cohort to Determine the Level and Durability of Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses after Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination
Abstract
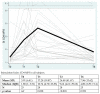
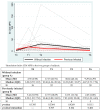
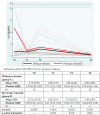
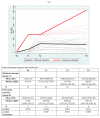
We prospectively studied immunological response against SARS-CoV-2 after vaccination among healthcare workers without (group A) and with previous infection (group B). The analyses were collected at T0 (before the BNT162b2), T1 (before the second dose), T2 and T6 (1 and 6 months after the second dose). For cellular immune response, the activation-induced cell marker assay was performed with CD4 and CD8 Spike peptide megapools expressed as Stimulation Index. For humoral immune response, we determined antibodies to Spike-1 and nucleocapsid protein. The linear mixed model compared specific times to T0. The CD4+ Spike response overall rate of change was significant at T1 (p = 0.038) and at T2 (p < 0.001), while decreasing at T6. For CD8+ Spike reactivity, the interaction between the time and group was significant (p = 0.0265), and the p value for group comparison was significant at the baseline (p = 0.0030) with higher SI in previously infected subjects. Overall, the anti-S Abs significantly increased from T1 to T6 compared to T0. The group B at T6 retained high anti-S titer (p < 0.001). At T6, in both groups we found a persistent humoral response and a high CD4+ T cell response able to cross recognize SARS-COV-2 variants including epsilon, even if not a circulating virus at that time.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; cellular and humoral immune responses; second dose; variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Outside the submitted work: C.D. has received speaker honoraria from Angelini, Novartis, Gilead, ViiV andShinogi. A.D.B. reports a hospital grant from Gilead and consultancy for ViiV, Janssen, MSD, Gilead and Abbvie. L.T. reports consultancy for ViiV, Gilead and Janssen. A. Sette is a consultant for Gritstone, Flow Pharma, CellCarta, Arcturus, Oxfordimmunotech and Avalia. M. B. serves on the scientific advisory boards for Angelini, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Cubist, Pfizer, Menarini, MSD, Nabriva, Paratek, Roche, Shionogi, Tetraphase, The Medicine Company and Astellas Pharma Inc, and has received funding for travel or speaker honoraria from Algorithm, Angelini, Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca, Cubist, Pfizer, MSD, Gilead Sciences, Menarini, Novartis, Ranbaxy and Teva. A.S. is a consultant for Gritstone Bio, Flow Pharma, Arcturus Therapeutics, ImmunoScape, CellCarta, Avalia, Moderna, Fortress, Repertoire and Astrazeneca. LJI has filed for patent protection for various aspects of T cell epitope and vaccine design work.
Figures

References
-
- Reynolds C.J., Pade C., Gibbons J.M., Butler D.K., Otter A.D., Menacho K., Fontana M., Smit A., Sackville-West J.E., Cutrino-Moguel T., et al. Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection rescues B and T cell responses to variants after first vaccine dose. Science. 2021;30:eabh1282. doi: 10.1126/science.abh1282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Painter M.M., Mathew D., Goel R.R., Apostolidis S.A., Pattekar A., Kuthuru O., Baxter A.E., Herati R.S., Oldridge D.A., Gouma S., et al. Rapid induction of antigen-specific CD4(+) T cells is associated with coordinated humoral and cellular immunity to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination. Immunity. 2021;54:2133–2142.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

