Mapping Potential Vaccine Candidates Predicted by VaxiJen for Different Viral Pathogens between 2017-2021-A Scoping Review
- PMID: 36366294
- PMCID: PMC9695814
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10111785
Mapping Potential Vaccine Candidates Predicted by VaxiJen for Different Viral Pathogens between 2017-2021-A Scoping Review
Abstract
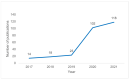
Reverse vaccinology (RV) is a promising alternative to traditional vaccinology. RV focuses on in silico methods to identify antigens or potential vaccine candidates (PVCs) from a pathogen's proteome. Researchers use VaxiJen, the most well-known RV tool, to predict PVCs for various pathogens. The purpose of this scoping review is to provide an overview of PVCs predicted by VaxiJen for different viruses between 2017 and 2021 using Arksey and O'Malley's framework and the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines. We used the term 'vaxijen' to search PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, EBSCOhost, and ProQuest One Academic. The protocol was registered at the Open Science Framework (OSF). We identified articles on this topic, charted them, and discussed the key findings. The database searches yielded 1033 articles, of which 275 were eligible. Most studies focused on severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), published between 2020 and 2021. Only a few articles (8/275; 2.9%) conducted experimental validations to confirm the predictions as vaccine candidates, with 2.2% (6/275) articles mentioning recombinant protein expression. Researchers commonly targeted parts of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein, with the frequently predicted epitopes as PVCs being major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I T cell epitopes WTAGAAAYY, RQIAPGQTG, IAIVMVTIM, and B cell epitope IAPGQTGKIADY, among others. The findings of this review are promising for the development of novel vaccines. We recommend that vaccinologists use these findings as a guide to performing experimental validation for various viruses, with SARS-CoV-2 as a priority, because better vaccines are needed, especially to stay ahead of the emergence of new variants. If successful, these vaccines could provide broader protection than traditional vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 vaccines; SARS-CoV-2; VaxiJen; antigens; reverse vaccinology; scoping review; vaccines; vaccinology; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . The Global Eradication of Smallpox: Final Report of the Global Commission for the Certification of Smallpox Eradication, Geneva, December 1979. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 1980.
-
- Rappuoli R., Del Giudice G. Vaccines: From Concept to Clinic. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 1999. Identification of vaccine targets; pp. 1–17.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous