The Advantage of Using Immunoinformatic Tools on Vaccine Design and Development for Coronavirus
- PMID: 36366353
- PMCID: PMC9693616
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10111844
The Advantage of Using Immunoinformatic Tools on Vaccine Design and Development for Coronavirus
Abstract
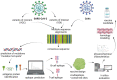
After the outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 by the end of 2019, the vaccine development strategies became a worldwide priority. Furthermore, the appearances of novel SARS-CoV-2 variants challenge researchers to develop new pharmacological or preventive strategies. However, vaccines still represent an efficient way to control the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic worldwide. This review describes the importance of bioinformatic and immunoinformatic tools (in silico) for guide vaccine design. In silico strategies permit the identification of epitopes (immunogenic peptides) which could be used as potential vaccines, as well as nonacarriers such as: vector viral based vaccines, RNA-based vaccines and dendrimers through immunoinformatics. Currently, nucleic acid and protein sequential as well structural analyses through bioinformatic tools allow us to get immunogenic epitopes which can induce immune response alone or in complex with nanocarriers. One of the advantages of in silico techniques is that they facilitate the identification of epitopes, while accelerating the process and helping to economize some stages of the development of safe vaccines.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; bioinformatics; epitope; immunoinformatics; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunoinformatics-Based Identification of B and T Cell Epitopes in RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase of SARS-CoV-2.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Oct 3;10(10):1660. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10101660. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36298525 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-epitope vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 applying immunoinformatics and molecular dynamics simulation approaches.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022 Apr;40(7):2917-2933. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1844060. Epub 2020 Nov 9. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022. PMID: 33164664 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics approach to epitope-based vaccine design against the SARS-CoV-2 in Bangladeshi patients.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022 Sep 20;20(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s43141-022-00410-8. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36125645 Free PMC article.
-
Recent trends in next generation immunoinformatics harnessed for universal coronavirus vaccine design.Pathog Glob Health. 2023 Mar;117(2):134-151. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2022.2072456. Epub 2022 May 12. Pathog Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 35550001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Better Epitope Discovery, Precision Immune Engineering, and Accelerated Vaccine Design Using Immunoinformatics Tools.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 7;11:442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00442. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32318055 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Design of multivalent-epitope vaccine models directed toward the world's population against HIV-Gag polyprotein: Reverse vaccinology and immunoinformatics.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 27;19(9):e0306559. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306559. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39331650 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Immunological Properties of a Chimeric Glycosyl Hydrolase 18 Based on Immunoinformatics Approaches: A Design of a New Anti-Leishmania Vaccine.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Dec 31;8(1):78-96. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00341. eCollection 2025 Jan 10. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39816796
-
In silico design of Ebola virus Glycoprotein antigenic peptides as vaccine candidates.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 28;20(3):e0319496. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319496. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40153397 Free PMC article.
-
Design of multi-epitope chimeric vaccine against Monkeypox virus and SARS-CoV-2: A vaccinomics perspective.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 May;28(10):e18452. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18452. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38801408 Free PMC article.
-
Biophysics of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein's receptor-binding domain interaction with ACE2 and neutralizing antibodies: from computation to functional insights.Biophys Rev. 2025 Mar 8;17(2):309-333. doi: 10.1007/s12551-025-01276-z. eCollection 2025 Apr. Biophys Rev. 2025. PMID: 40376405 Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

