Global Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Antibody Response and the Impact of Impulsive Drug Therapy
- PMID: 36366355
- PMCID: PMC9699126
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10111846
Global Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Infection with Antibody Response and the Impact of Impulsive Drug Therapy
Abstract
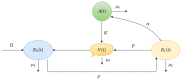
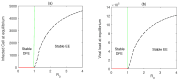
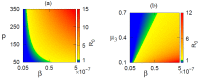
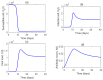
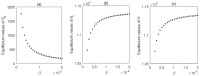
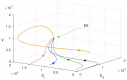
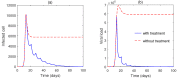
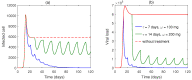
Mathematical modeling is crucial to investigating tthe ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. The primary target area of the SARS-CoV-2 virus is epithelial cells in the human lower respiratory tract. During this viral infection, infected cells can activate innate and adaptive immune responses to viral infection. Immune response in COVID-19 infection can lead to longer recovery time and more severe secondary complications. We formulate a micro-level mathematical model by incorporating a saturation term for SARS-CoV-2-infected epithelial cell loss reliant on infected cell levels. Forward and backward bifurcation between disease-free and endemic equilibrium points have been analyzed. Global stability of both disease-free and endemic equilibrium is provided. We have seen that the disease-free equilibrium is globally stable for R0<1, and endemic equilibrium exists and is globally stable for R0>1. Impulsive application of drug dosing has been applied for the treatment of COVID-19 patients. Additionally, the dynamics of the impulsive system are discussed when a patient takes drug holidays. Numerical simulations support the analytical findings and the dynamical regimes in the systems.
Keywords: antibody response; basic reproduction number; drug holidays; epithelial cell; impulsive control; transcritical bifurcation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamical demeanour of SARS-CoV-2 virus undergoing immune response mechanism in COVID-19 pandemic.Eur Phys J Spec Top. 2022;231(18-20):3357-3370. doi: 10.1140/epjs/s11734-022-00437-5. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Eur Phys J Spec Top. 2022. PMID: 35075384 Free PMC article.
-
Within Host Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in Humans: Modeling Immune Responses and Antiviral Treatments.SN Comput Sci. 2021;2(6):482. doi: 10.1007/s42979-021-00919-8. Epub 2021 Oct 12. SN Comput Sci. 2021. PMID: 34661166 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical modeling of COVID-19 transmission: the roles of intervention strategies and lockdown.Math Biosci Eng. 2020 Sep 10;17(5):5961-5986. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2020318. Math Biosci Eng. 2020. PMID: 33120585
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and pregnancy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun;222(6):521-531. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.03.021. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32217113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Killer Cells in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Implications.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 30;13:888248. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.888248. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844604 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vaccine and antiviral drug promise for preventing post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, and their combination for its treatment.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1329162. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1329162. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39185419 Free PMC article.
-
A Managerial Approach towards Modeling the Different Strains of the COVID-19 Virus Based on the Spatial GeoCity Model.Viruses. 2023 Nov 23;15(12):2299. doi: 10.3390/v15122299. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38140541 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delikhoon M., Guzman M.I., Nabizadeh R., Norouzian Baghani A. Modes of transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) and factors influencing on the airborne transmission: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021;18:395. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18020395. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carsetti R., Zaffina S., Piano Mortari E., Terreri S., Corrente F., Capponi C., Palomba P., Mirabella M., Cascioli S., Palange P., et al. Different Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Asymptomatic, Mild, and Severe Cases. Front. Immunol. 2020;11:3365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.610300. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

