Omicron Variant Generates a Higher and More Sustained Viral Load in Nasopharynx and Saliva Than the Delta Variant of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 36366518
- PMCID: PMC9696014
- DOI: 10.3390/v14112420
Omicron Variant Generates a Higher and More Sustained Viral Load in Nasopharynx and Saliva Than the Delta Variant of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
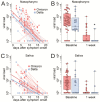
The Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 spreads more easily than earlier variants, possibly as a result of a higher viral load in the upper respiratory tract and oral cavity. Hence, we investigated whether the Omicron variant generates a higher viral load than that of the Delta variant in saliva and nasopharynx. Both specimens were collected from 52 Omicron and 17 Delta cases at two time points one week apart and analyzed by qRT-PCR. Viral load was measured as 10 log RNA genome copies per 1000 human cells according to the WHO reference standard. We found that Omicron cases carried a higher viral load and had more sustained viral shedding compared to the Delta cases, especially in the nasopharynx.
Keywords: Delta variant; Norway; Omicron variant; SARS-CoV-2; viral load.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern 2021 [updated 26 Nov 2021] [(accessed on 26 October 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.....
-
- Brandal L.T., MacDonald E., Veneti L., Ravlo T., Lange H., Naseer U., Feruglio S., Bragstad K., Hungnes O., Ødeskaug L.E., et al. Outbreak caused by the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in Norway, November to December 2021. Eurosurveillance. 2021;26:2101147. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.50.2101147. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garrett N., Tapley A., Andriesen J., Seocharan I., Fisher L.H., Bunts L., Espy N., Wallis C.L., Randhawa A.K., Ketter N., et al. High Rate of Asymptomatic Carriage Associated with Variant Strain Omicron. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.12.20.21268130. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

