Pooled genetic screens with image-based profiling
- PMID: 36366905
- PMCID: PMC9650298
- DOI: 10.15252/msb.202110768
Pooled genetic screens with image-based profiling
Abstract
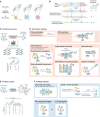
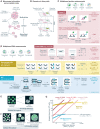
Spatial structure in biology, spanning molecular, organellular, cellular, tissue, and organismal scales, is encoded through a combination of genetic and epigenetic factors in individual cells. Microscopy remains the most direct approach to exploring the intricate spatial complexity defining biological systems and the structured dynamic responses of these systems to perturbations. Genetic screens with deep single-cell profiling via image features or gene expression programs have the capacity to show how biological systems work in detail by cataloging many cellular phenotypes with one experimental assay. Microscopy-based cellular profiling provides information complementary to next-generation sequencing (NGS) profiling and has only recently become compatible with large-scale genetic screens. Optical screening now offers the scale needed for systematic characterization and is poised for further scale-up. We discuss how these methodologies, together with emerging technologies for genetic perturbation and microscopy-based multiplexed molecular phenotyping, are powering new approaches to reveal genotype-phenotype relationships.
Keywords: morphological profiling; multiplexed imaging; optical microscopy profiling; optical screening; pooled genetic screening.
© 2022 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pooled genetic perturbation screens with image-based phenotypes.Nat Protoc. 2022 Feb;17(2):476-512. doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00653-8. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Nat Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35022620 Free PMC article.
-
Optical Pooled Screens in Human Cells.Cell. 2019 Oct 17;179(3):787-799.e17. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.09.016. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31626775 Free PMC article.
-
Image-based cell phenotyping with deep learning.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021 Dec;65:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 May 21. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34023800 Review.
-
Pooled Genome-Scale CRISPR Screens in Single Cells.Annu Rev Genet. 2023 Nov 27;57:223-244. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-072920-013842. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Annu Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 37562410 Review.
-
Large-scale image-based profiling of single-cell phenotypes in arrayed CRISPR-Cas9 gene perturbation screens.Mol Syst Biol. 2018 Jan 23;14(1):e8064. doi: 10.15252/msb.20178064. Mol Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29363560 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cell Painting PLUS: expanding the multiplexing capacity of Cell Painting-based phenotypic profiling using iterative staining-elution cycles.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 24;16(1):3857. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58765-8. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40274798 Free PMC article.
-
Using Transcriptomics and Cell Morphology Data in Drug Discovery: The Long Road to Practice.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023 Mar 22;14(4):386-395. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00015. eCollection 2023 Apr 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 37077392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphological profiling for drug discovery in the era of deep learning.Brief Bioinform. 2024 May 23;25(4):bbae284. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae284. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38886164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking autism risk genes to morphological and pharmaceutical screening by high-content imaging: Future directions and opinion.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025 Aug;79(8):435-446. doi: 10.1111/pcn.13847. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40492449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A genome-wide atlas of human cell morphology.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Aug 7:2023.08.06.552164. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.06.552164. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Nat Methods. 2025 Mar;22(3):621-633. doi: 10.1038/s41592-024-02537-7. PMID: 37609130 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

