Antibiotic resistance surveillance of Klebsiella pneumoniae complex is affected by refined MALDI-TOF identification, Swiss data, 2017 to 2022
- PMID: 36367012
- PMCID: PMC9650708
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.45.2200104
Antibiotic resistance surveillance of Klebsiella pneumoniae complex is affected by refined MALDI-TOF identification, Swiss data, 2017 to 2022
Abstract
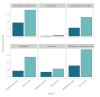
BackgroundModern laboratory methods such as next generation sequencing and MALDI-TOF allow identification of novel bacterial species. This can affect surveillance of infections and antimicrobial resistance. From 2017, increasing numbers of medical microbiology laboratories in Switzerland differentiated Klebsiella variicola from Klebsiella pneumoniae complex using updated MALDI-TOF databases, whereas many laboratories still report them as K. pneumoniae or K. pneumoniae complex.AimOur study explored whether separate reporting of K. variicola and the Klebsiella pneumoniae complex affected the ANRESIS surveillance database.MethodsWe analysed antibiotic susceptibility rates and specimen types of K. variicola and non-K. variicola-K. pneumoniae complex isolates reported by Swiss medical laboratories to the ANRESIS database (Swiss Centre for Antibiotic Resistance) from January 2017 to June 2022.ResultsAnalysis of Swiss antimicrobial resistance data revealed increased susceptibility rates of K. variicola compared with species of the K. pneumoniae complex other than K. variicola in all six antibiotic classes tested. This can lead to underestimated resistance rates of K. pneumoniae complex in laboratories that do not specifically identify K. variicola. Furthermore, K. variicola strains were significantly more often reported from blood and primarily sterile specimens than isolates of the K. pneumoniae complex other than K. variicola, indicating increased invasiveness of K. variicola.ConclusionOur data suggest that refined differentiation of the K. pneumoniae complex can improve our understanding of its taxonomy, susceptibility, epidemiology and clinical significance, thus providing more precise information to clinicians and epidemiologists.
Keywords: ANRESIS; Klebsiella pneumoniae complex; Klebsiella variicola; antimicrobial resistance; surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Holt KE, Wertheim H, Zadoks RN, Baker S, Whitehouse CA, Dance D, et al. Genomic analysis of diversity, population structure, virulence, and antimicrobial resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae, an urgent threat to public health. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(27):E3574-81. 10.1073/pnas.1501049112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources